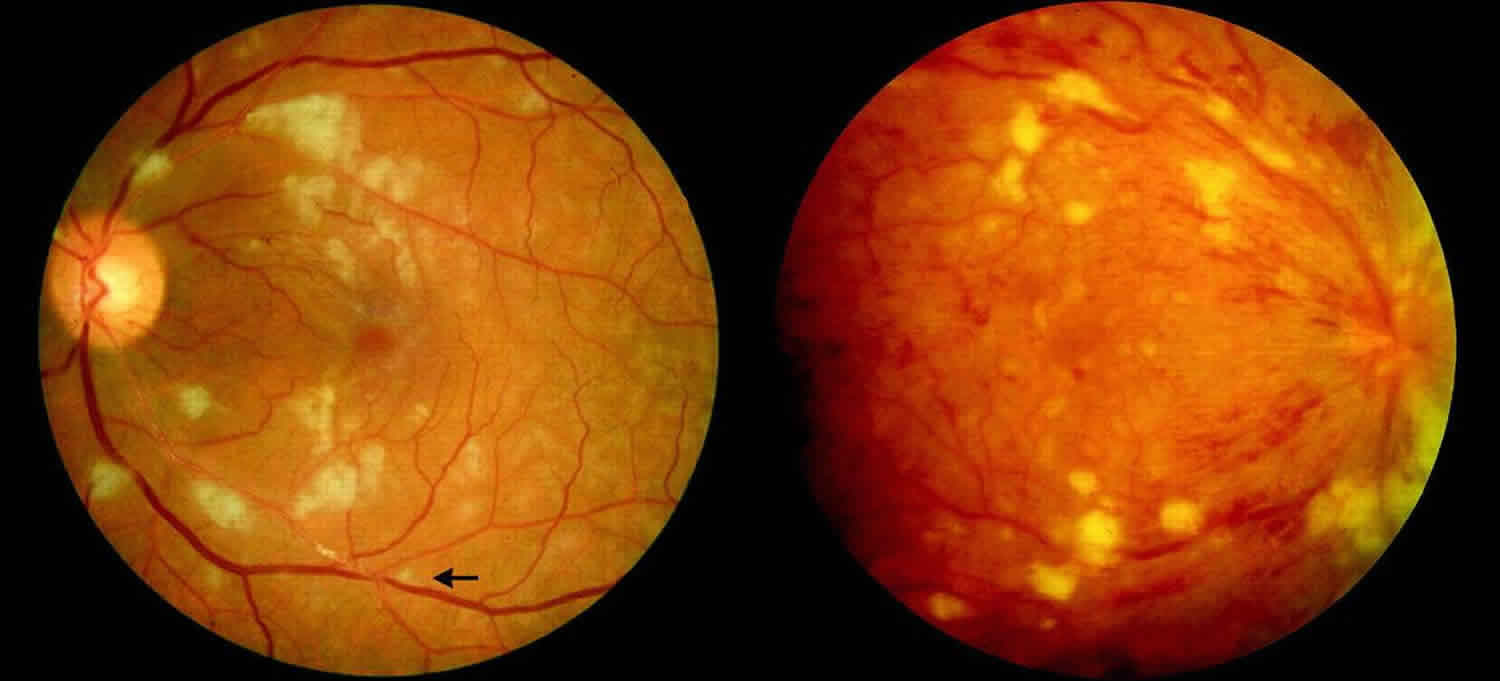
Fundus color photographs showing cottonwool spots, exudates, multiple... Download Scientific
Key Points Manifestations of diabetic retinopathy include microaneurysms, intraretinal hemorrhage, exudates, macular edema, macular ischemia, neovascularization, vitreous hemorrhage, and traction retinal detachment. Symptoms may not develop until late in the disease.

Cottonwool spots American Academy of Ophthalmology
Cotton wool spots in the distribution of a branch retinal artery, corroborated by fluorescein angiography, suggest BRAO. Classification of BRAO can also be subdivided by its temporal profile and the particular vessels implicated. BRAO may be described as permanent BRAO, transient BRAO, or cilioretinal artery occlusion (CLRAO), specifically.

Solitary cottonwool spot in the right eye ofa patient with PGL who... Download Scientific Diagram
One of these potential retinal findings is the cotton wool spot (CWS). A CWS appears as a white and fluffy superficial lesion 0.1mm to 1.0mm in diameter that obscures the underlying retinal detail. 1,2 This small but important finding can be a marker for potentially life-threatening conditions, making it of great clinical utility.
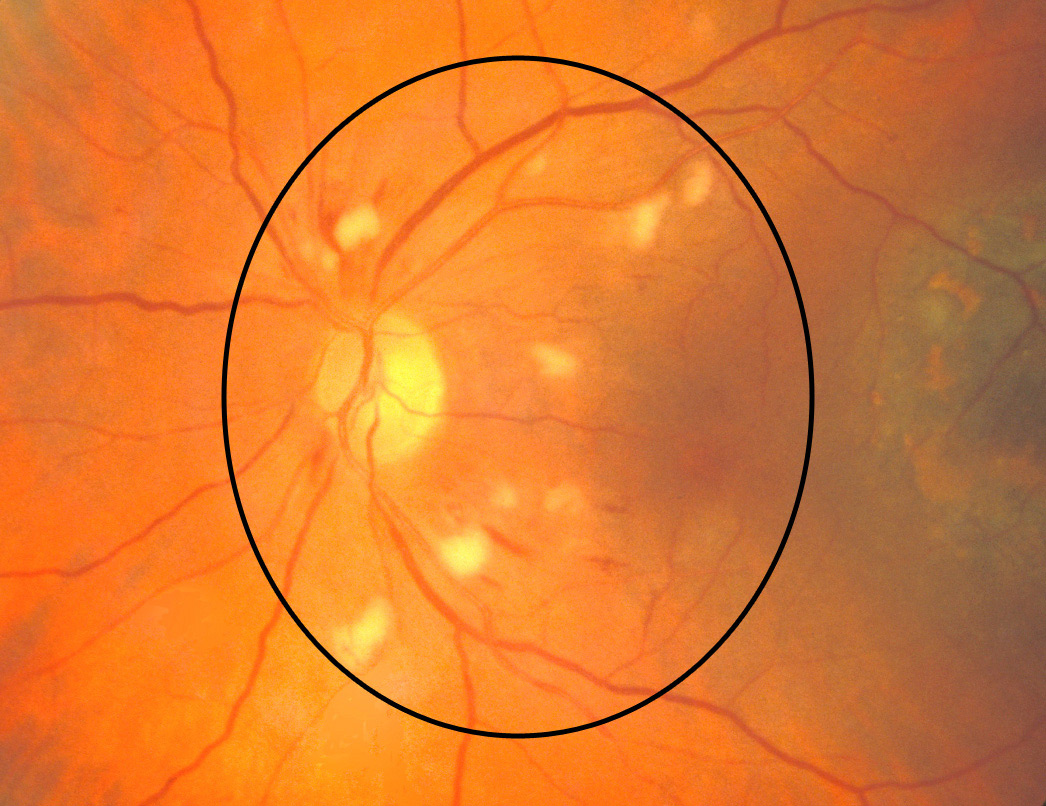
Cotton wool spots. COMS Grading Scheme
Axonal myelination in the human central nervous system is a complex, orderly process carried out by oligodendrocyte progenitor cells, which migrate under the influence of neuro-hormonal signals to generate oligodendrocytes that produce myelin.

Why cotton wool spots should not be regarded as retinal nerve fibre layer infarcts British
1. "Cotton wool" spots When blood clots prevent nutrients from getting to the retina, the tissue in the retina begins to swell and die. If the doctor examines your eye closely using optical coherence tomography, this area looks white and fluffy like cotton wool (shown in the image above). These spots do not typically affect a person's vision. 2.

Hypertensive Retinopathy Ento Key
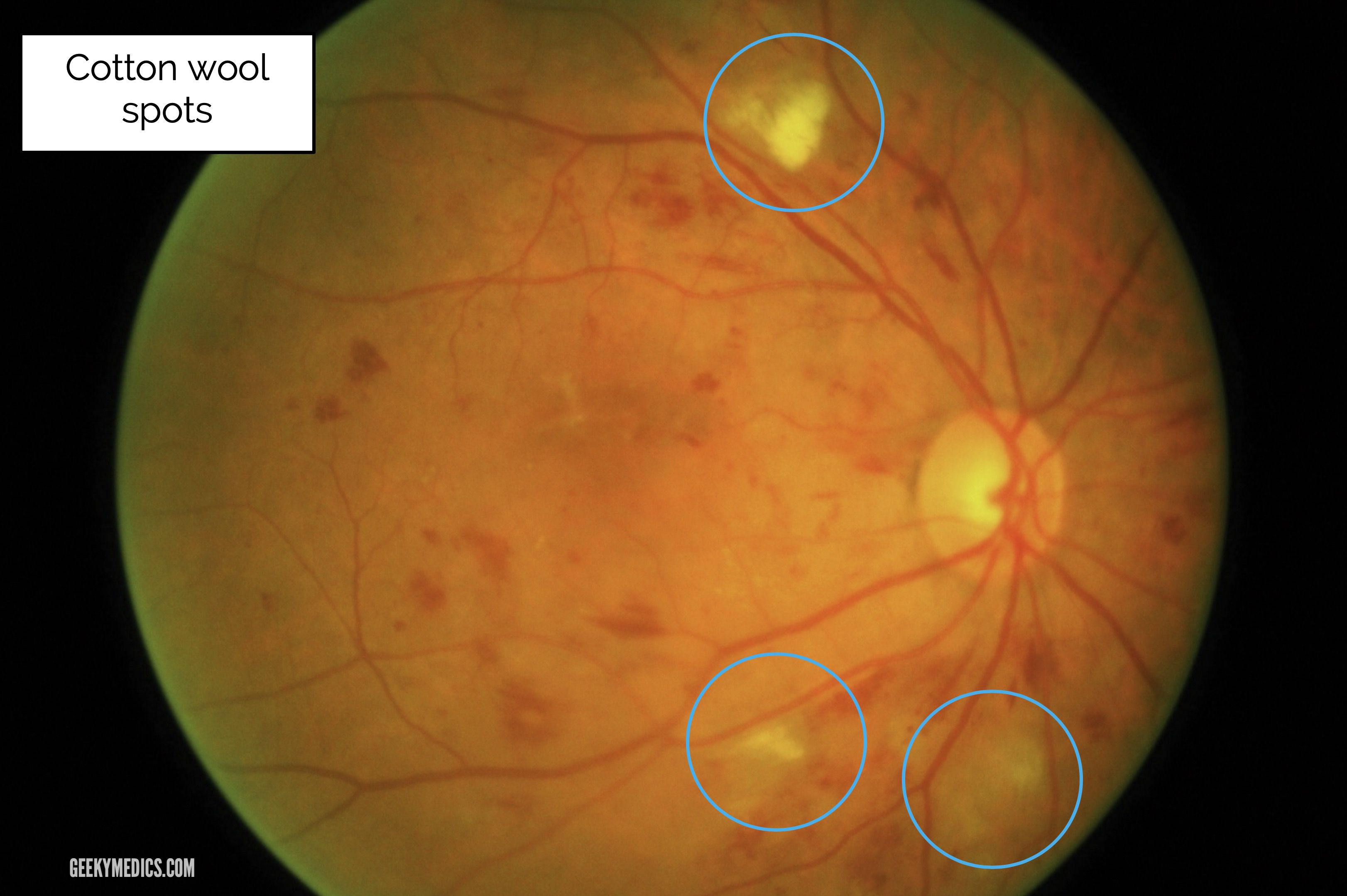
Cotton wool spots are opaque fluffy white patches on the retina of the eye that are considered an abnormal finding during a funduscopic exam (also called an ophthalmoscopic exam). [1] Cotton wool spots are typically a sign of another disease state, most common of which is diabetic retinopathy. [2]
Cotton Wool Spots Causes and Symptoms
Purtscher retinopathy has since been described as a chorioretinopahy associated with indirect trauma, non-ocular injury, associated with a constellation of retinal findings including cotton-wool spots, retinal hemorrhages, optic disc edema, and Purtscher flecken (areas of inner retinal whitening).

Retinal Images BARS
The retinopathy associated with SLE is the most common type of posterior segment finding and the risk of retinal involvement varies with disease control. It may range from 3 percent in well-controlled patients to 29 percent in patients with more active systemic disease. 6,7 The most common retinal manifestation is cotton wool spots ( See Figure.
Cotton wool spots, causes, symptoms, diagnosis & treatment
Chris A. Knobbe, MD Eye strokes occur when blockages (occlusions) occur in arteries or veins in the retina, causing vision loss. The severity of vision loss depends on the extent and location of the occlusion (s) and loss of blood flow.

Why cotton wool spots should not be regarded as retinal nerve fibre layer infarcts McLeod 89
A cotton-wool spot is the name given to a small white spot in the retina that resembles cotton wool (raw cotton). The retina in your eye is like the film inside a camera. The retina "takes the picture" of objects you look at and sends the message to the brain. The retina is a living tissue, which requires blood supplied by tiny vessels.
Cotton wool spots. COMS Grading Scheme
Cotton-wool spots Retinal vasculitis may result in micro-infarcts of the retinal nerve fiber layer that manifests as diffuse, fluffy, cotton-wool like spots in the superficial retinal surface. [1] [12] Systemic vasculitidis such as systemic lupus erythematosus, [36] polyarteritis nodosa, [37] Churg-Strauss syndrome [38] can be associated with.

Why cotton wool spots should not be regarded as retinal nerve fibre layer infarcts British
Introduction Hypertension is a risk factor for systemic conditions that can lead to target-organ damage. Specifically, hypertension may lead to multiple adverse effects to the eye that can inevitably cause cause retinopathy, optic neuropathy, and choroidopathy.

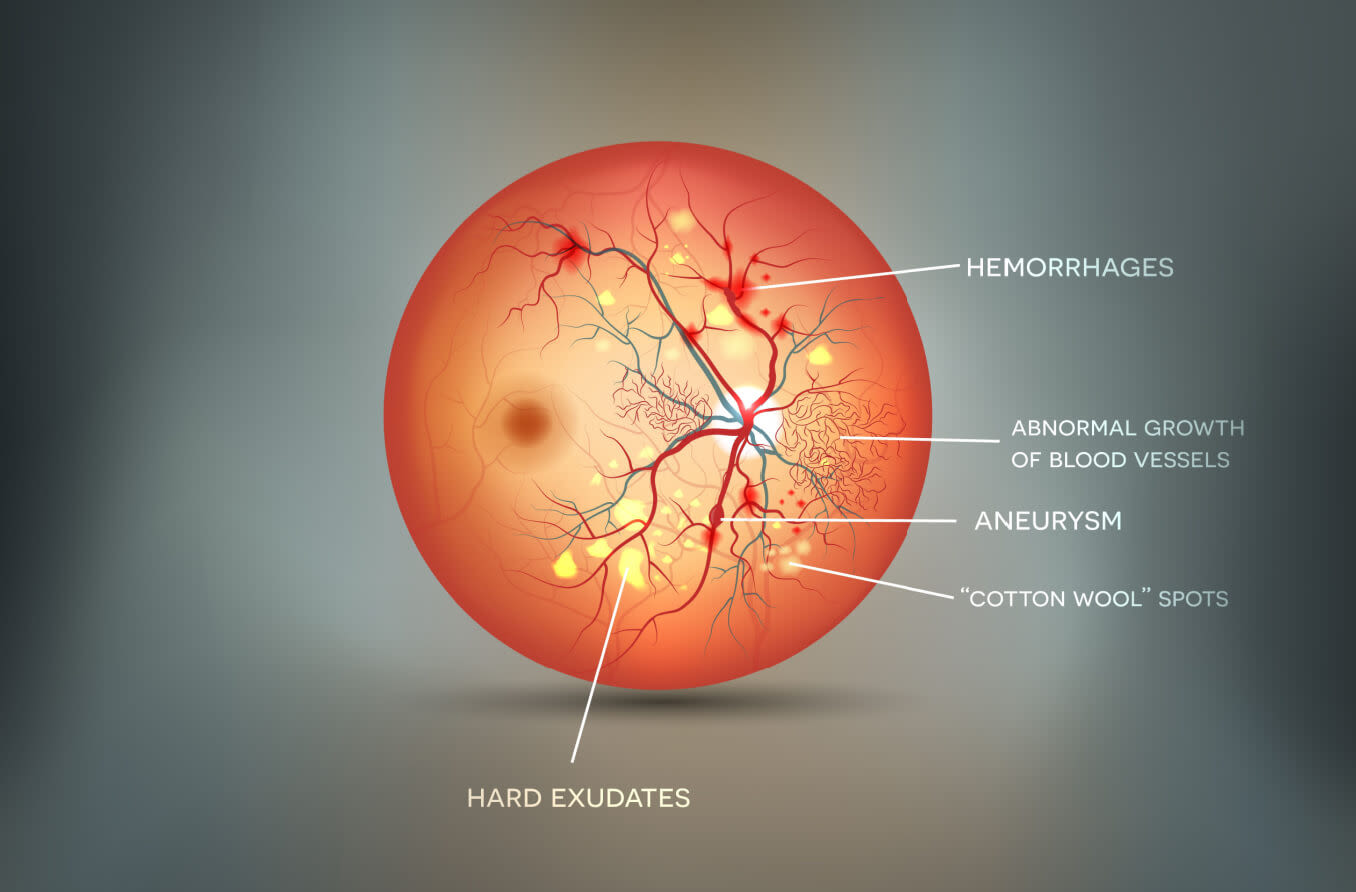
A sample retinal image with cotton wool spots and hemorrhages. Download Scientific Diagram
Retinal cotton-wool spots. In contrast to a vascular occlusion of the precapillary arterial flow, mechanical distortion or traumatic laceration of the nerve fiber layer can also result in the interruption of axoplasmic flow and the development of a cotton-wool spot.

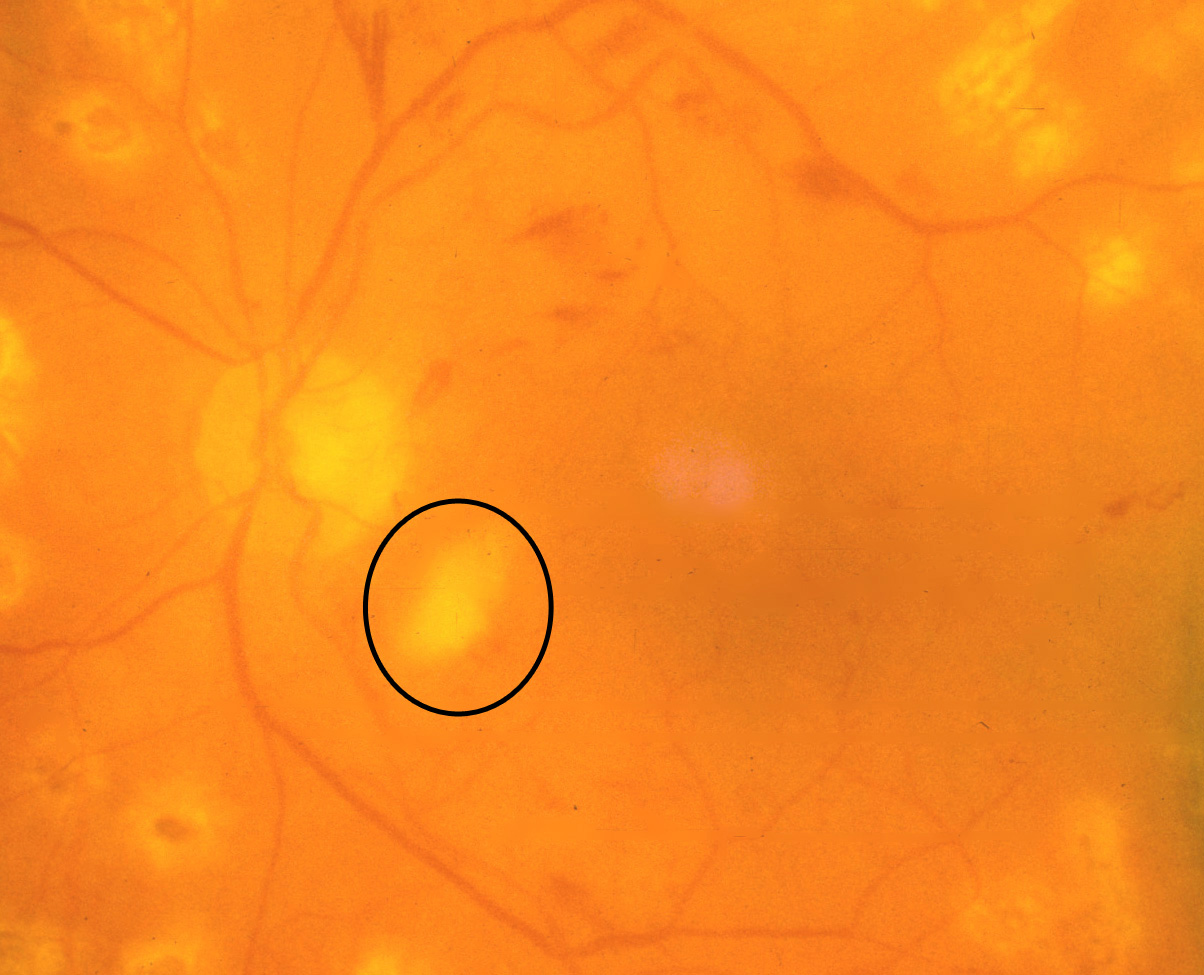
Cotton wool spot in retinal fundus image (in black circle) [32]. Download Scientific Diagram
Cotton-wool spots (CWSs) are retinal lesions, most commonly seen as manifestations of diabetes mellitus and systemic hypertension. They are also associated with a number of other etiologies including ischemic, embolic, connective tissue, neoplastic, and infectious, 1, 2 but occasionally no underlying cause can be identified. 2

Cotton Wool Spots Caused by microinfarcts. Exploded GrepMed
Cotton wool spots (CWS) are fluffy white or yellow spots that can appear on the retina. While the spots themselves don't typically cause problems, they often indicate an underlying condition. A CWS can be a cause for concern in an otherwise healthy individual. What causes cotton wool spots?
Fundoscopic Appearances of Retinal Pathologies Geeky Medics
A cotton-wool spot, or soft exudate, is a yellow-white lesion in the superficial retina that usually occupies an area less than one fourth that of the optic disc ( Fig. 69-19 ). A cotton-wool spot can occur singly or in conjunction with many others ( Fig. 69-20 ).