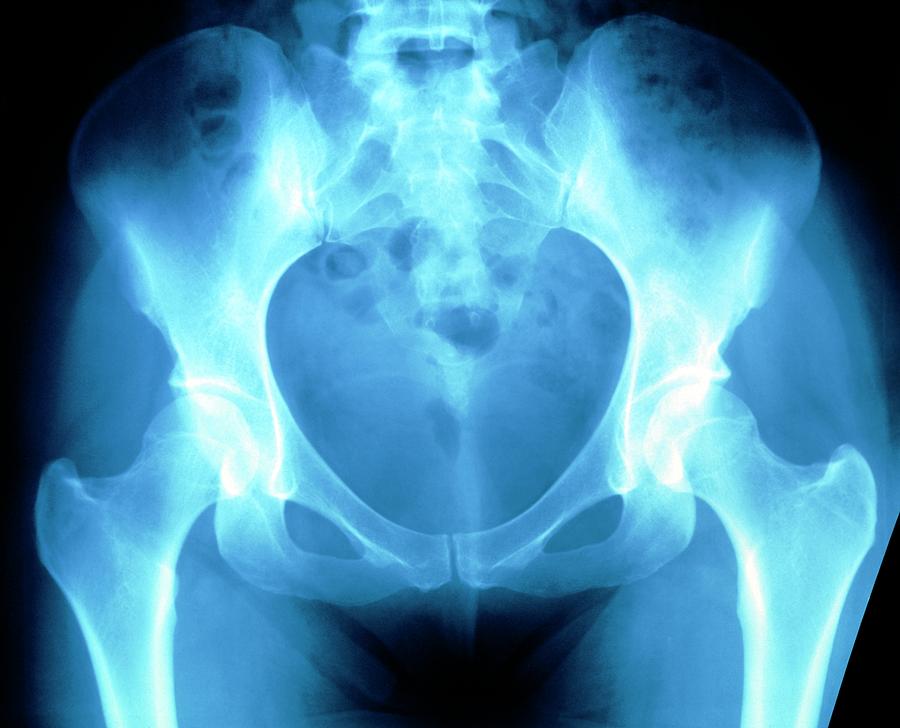
Falsecolour Xray Of A Normal Adult Female Pelvis Photograph by Science Photo Library Fine
The pelvis series is comprised of an anteroposterior (AP) with additional projections based on indications and pathology. The series is used most in emergency departments during the evaluation of multi-trauma patients due to the complex anatomy the AP projection covers. The pelvis series examines the main pelvic ring, obturator foramina.

Xray Of Female Pelvis And Lower Back Stock Photo Download Image Now iStock
Uterus / diagnostic imaging. This article provides an overview of ultrasonographic evaluation of the normal female pelvis. Pertinent pelvic anatomy is reviewed, and there is an in-depth discussion of the normal appearance of the uterus and ovaries. In addition, the indications and technique for performing 3-dimensional imaging..

AP Pelvis XRay Anatomy Diagram Quizlet
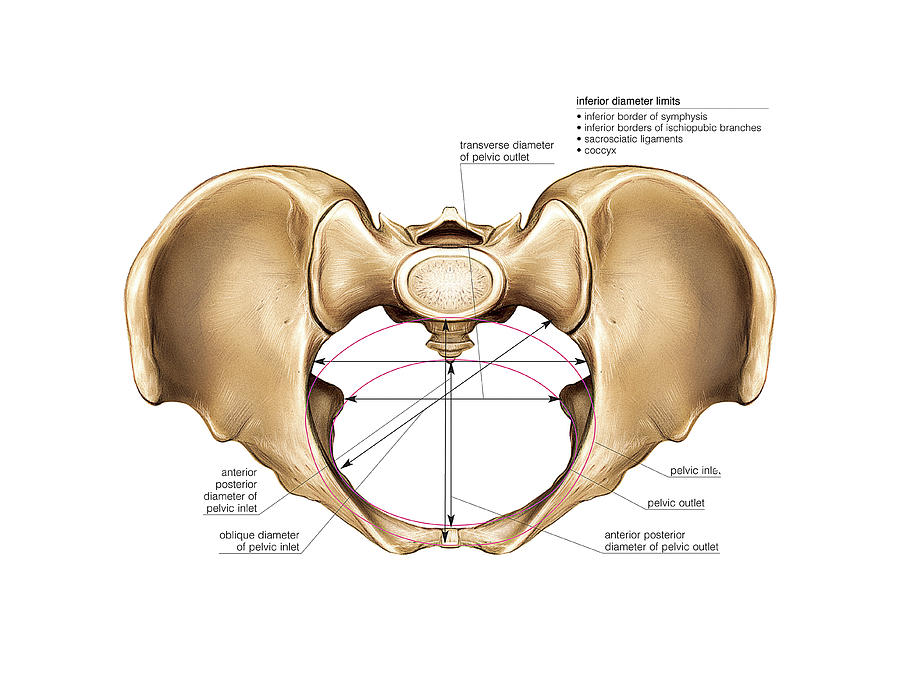
females: round or oval wider greater sciatic notch in females acetabulum faces more anteriorly in females sacrum more triangular and shorter in females oval or triangular obturator foramen in females The shape of the female bony pelvis can be described using the following terms 3: gynaecoid pelvis (50%): normal female type
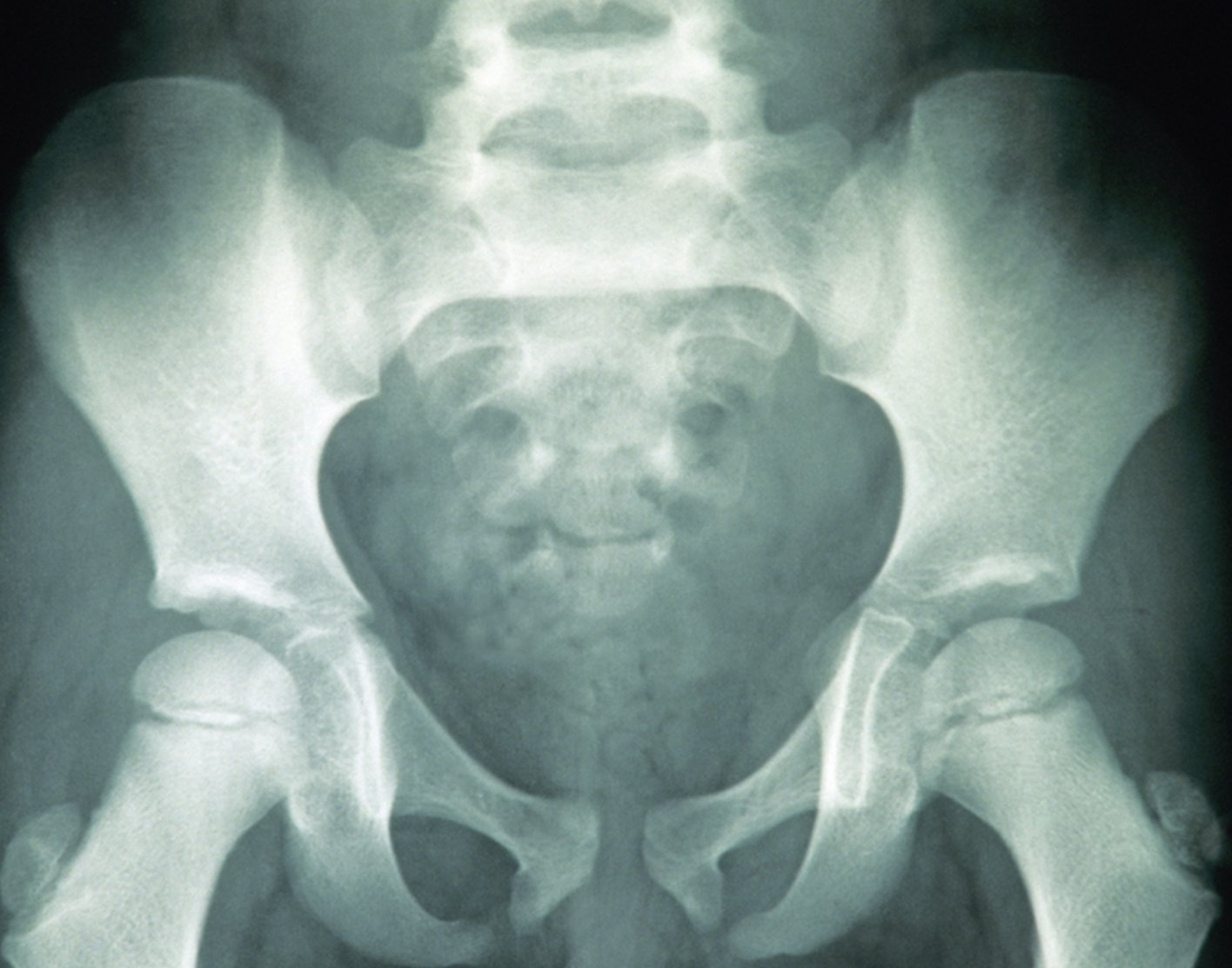
Pelvis xray
A pelvis x-ray, also known as a pelvis series or pelvis radiograph , is a single x-ray of the pelvis to include the iliac crests and pubic symphysis. It allows assessment of general pelvic pathology, the sacrum, some of the lower lumbar vertebra and the proximal femora. Reference article This is a summary article.

Anatomy of the female pelvis The BMJ
The 'uterus' is the Latin term for the womb and is located between the bladder and the rectum in the female pelvis. The uterus is a relatively superficial organ and can be imaged on a variety of modalities. Most commonly, ultrasound is the modality used for imaging the uterus. However, MRI comes a close second for evaluating uterine pathology. Other rarer modalities include hysterosonogram.
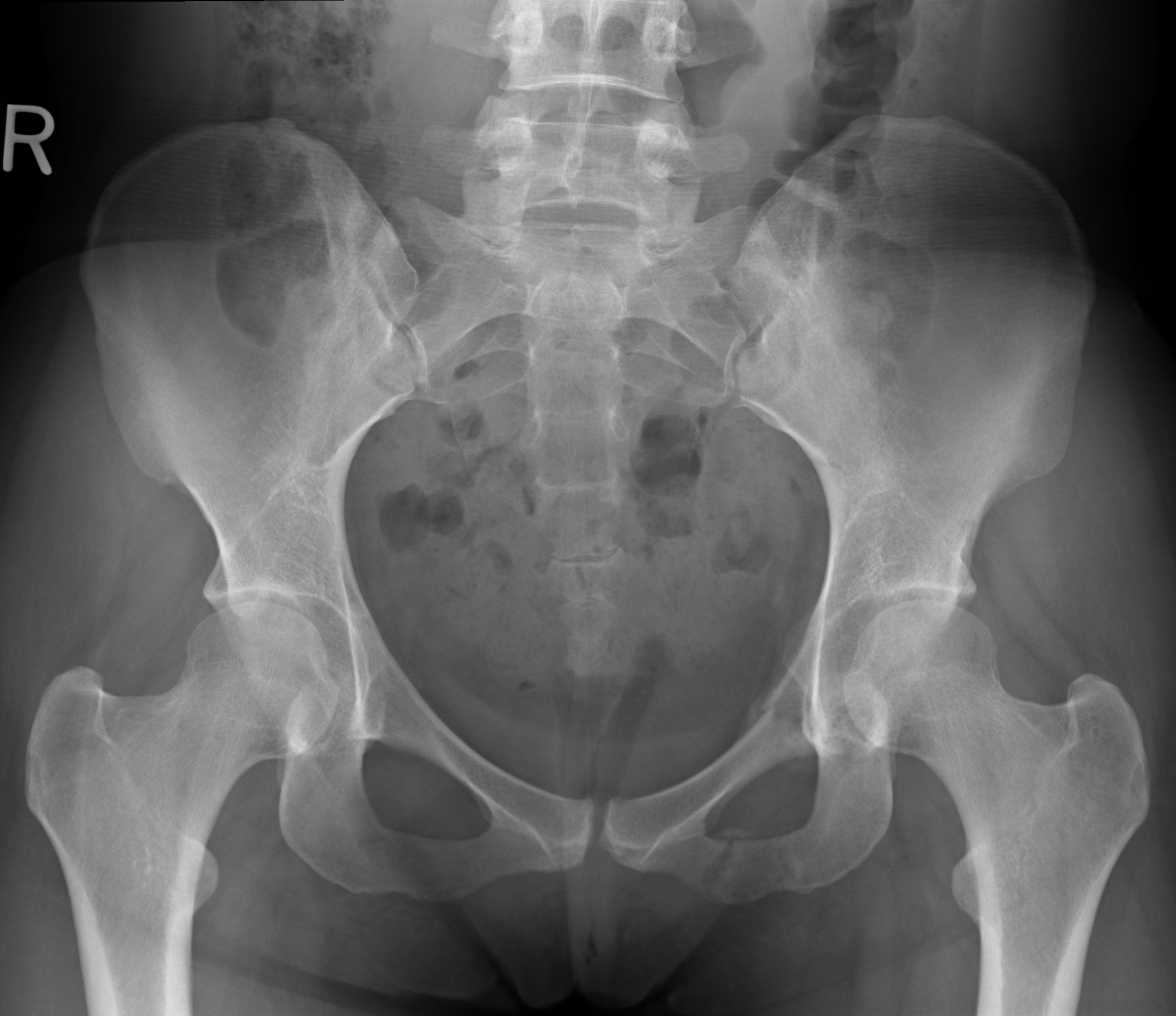
Xray of Normal Pelvis (Female) Eccles Health Sciences Library J. Willard Marriott Digital
This tutorial was a self-administered PowerPoint incorporating X-ray, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging, which are all often used for the pelvic region, as well as self-quizzing and clinical applications.
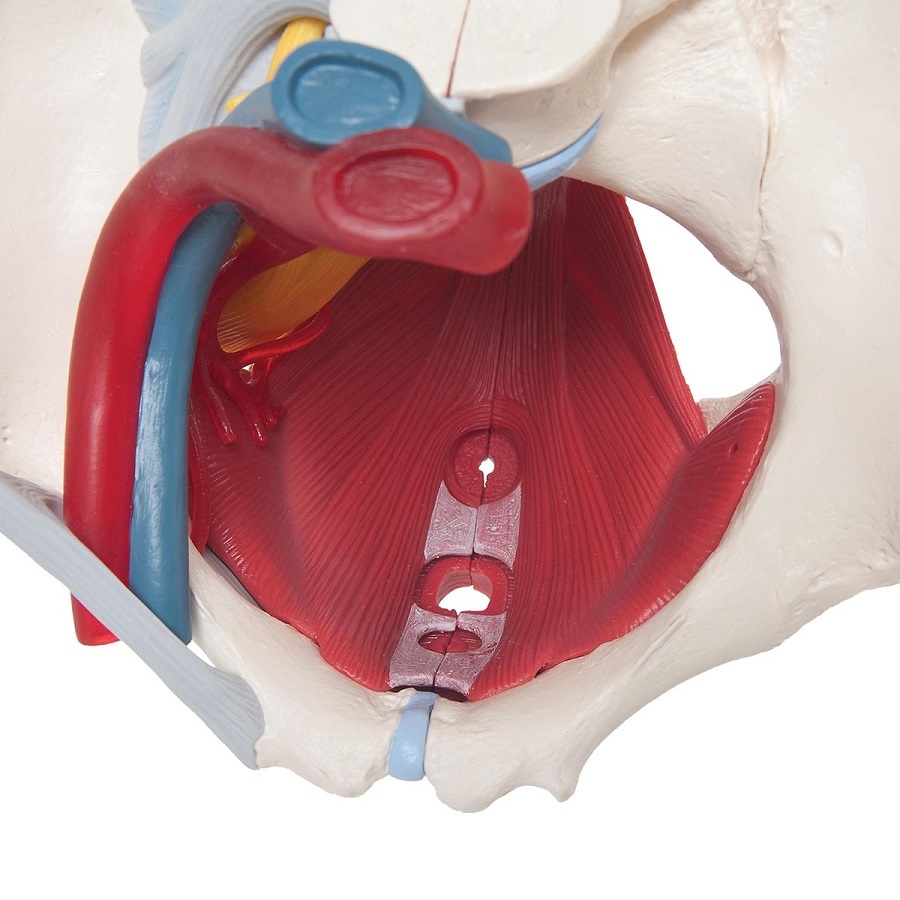
Anatomical Models of Female Pelvis with Ligaments, Vessels, Nerves, Pelvic Floor and Organs
Applied Radiological Anatomy - July 2012. To save this book to your Kindle, first ensure [email protected] is added to your Approved Personal Document E-mail List under your Personal Document Settings on the Manage Your Content and Devices page of your Amazon account.

Female Pelvic Pelivs Xray stock photo iStock
Numerous lines, arcs and stripes make up the pelvic radiograph (Figs. 1 and 2 ). The iliopectineal line extends from the iliac wing medial margin, along the superior margin of the superior pubic ramus, to the pubic symphysis. It delineates the pelvic anterior column. The ilioischial line starts from the iliac wing medial margin and extends to.

Female Pelvis Xray Stock Photo Download Image Now iStock
A pelvis X-ray (radiograph) is a medical imaging test that creates a black-and-white picture of your pelvic bones. Your pelvic bones include your hip bones (ilium, ischium and pubis), the triangle-shaped bone at the base of your spine (sacrum) and your tailbone (coccyx).

Pelvis Diagram Quizlet
Pelvic X-ray and Computed Tomography Techniques . The routine initial view of the pelvis is the anterior-posterior (AP) x-ray ( Figure 13-1 ).This image is obtained with the patient supine and the x-ray beam oriented 90 degrees to the patient's long axis, passing through the patient from anterior to posterior.
Female Pelvis Photograph by Asklepios Medical Atlas Fine Art America
Female Pelvis. The female external genitalia (vulva) extend from the mons pubis across the introitus (opening of the urethra and vagina) to the perineum. The internal genitalia consist of the uterine corpus, cervix, vagina, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. The pelvic organs are invested by peritoneum. Anterior to the uterus, the peritoneal cavity.

👨🏽💻Want to learn a system for reviewing a pelvic Xray? Read on to find out and swipe left to
It helps to assess joint dislocations and fractures (i.e. iliopectineal line, ilioischial line, Shenton line) in the trauma setting, as well as, bone lesions and degenerative diseases. A properly aligned AP pelvis view is imperative in the assessment of early hip degeneration, in particular for the assessment of femoroacetabular impingement.

Pelvic Xray Showing A Right Femoral Hemiarthroplasty Stock Photo & More Pictures of Adult iStock
Female pelvis bones. Hip bones. There are two hip bones, one on the left side of the body and the other on the right. Together, they form the part of the pelvis called the pelvic girdle.

Xray Of Female Pelvis Stock Photo Download Image Now Xray Image, Human Skeleton, Pelvis
Normal chest x ray. Radiological anatomy is where your human anatomy knowledge meets clinical practice. It gathers several non-invasive methods for visualizing the inner body structures. The most frequently used imaging modalities are radiography (X-ray), computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).X-ray and CT require the use of ionizing radiation while MRI uses a magnetic.

Pelvis Anatomy Recon Orthobullets
An X-ray of the pelvis focuses specifically on the area between your hips that holds many of your reproductive and digestive organs. Your pelvis is made up of three bones, the ilium, ischium, and.

Anatomical lines of the pelvis on an anterioposterior radiograph The BMJ
19.7K Description Pelvic X-Ray Anatomy and Interpretation Checklist - Sacro-iliac joints - Don't forget the lumbar spine - Are the pedicles present? - Iliac bone lesion? - Avulsion fracture - ASIS/AIIS - Trace the pelvic ring and obturator foramen - Acetabulum - Shenton's line - Neck of femur fracture?