
Abductor Pollicis Longus Learn Muscles
The adductor pollicis muscle plays an important role in opposition movements of the thumb. Opposition is the combined movement of the thumb where the pad of the thumb is brought into contact with the pads of one or more of the other fingers. If there is impaired nerve function to the adductor pollicis muscle, the individual has difficulty.

Musculus abductor pollicis brevis Stock Photo Alamy
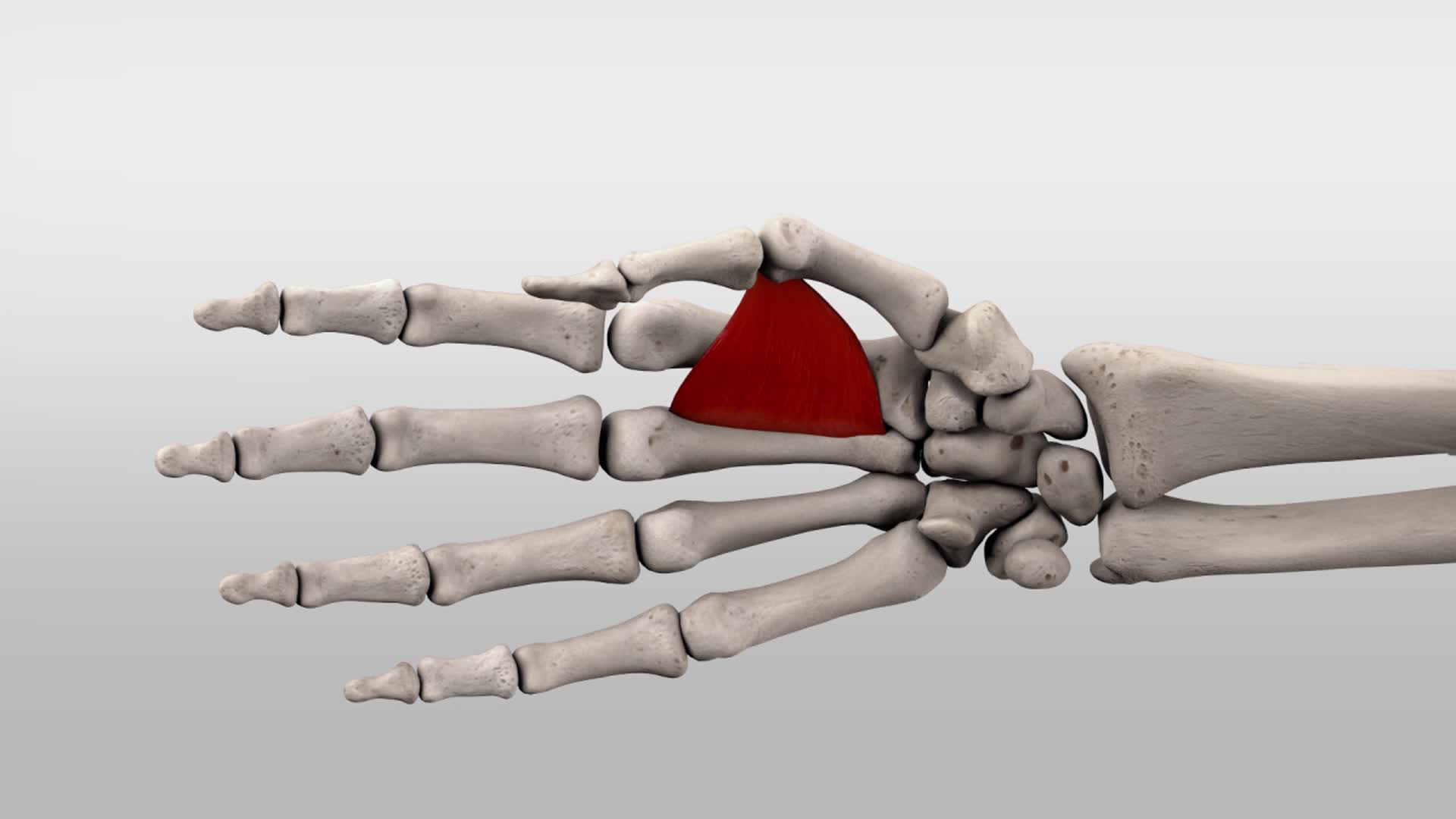
The adductor pollicis (Latin: musculus adductor pollicis) is a flat triangular-shaped muscle of the hand.Together with the abductor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis and opponens pollicis, it forms the thenar eminence.Therefore, the adductor pollicis is known as one of the four thenar muscles that lie on the lateral (radial) side of the palm.
Musculus adductor pollicis MedkoM
This video covers the most important muscle facts on the anatomy of the adductor pollicis muscle, one of the four thenar muscles: origin, insertion, innervat.

Adductor Pollicis The Trigger Point & Referred Pain Guide MUSCLE BALANCE/STRENGTH/REHAB
Dr. Ebraheim's educational animated video describes the anatomy of the adductor pollicis muscle.The abductor pollicis muscle is a small muscle of the hand an.
Musculus adductor pollicis DocCheck
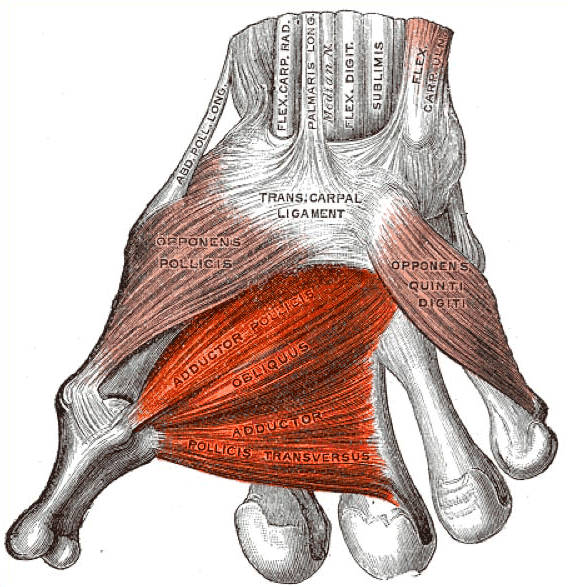
The adductor pollicis muscle is found in the adductor compartment of the hand. It is a fan-shaped skeletal muscle and is composed of two heads, which are named based on the orientation of their muscle fibers: - transverse head of adductor pollicis muscle. - anterior to the second metacarpal bone, and the first dorsal interosseous muscle of hand;
Adductor Pollicis (hand) Rehab My Patient
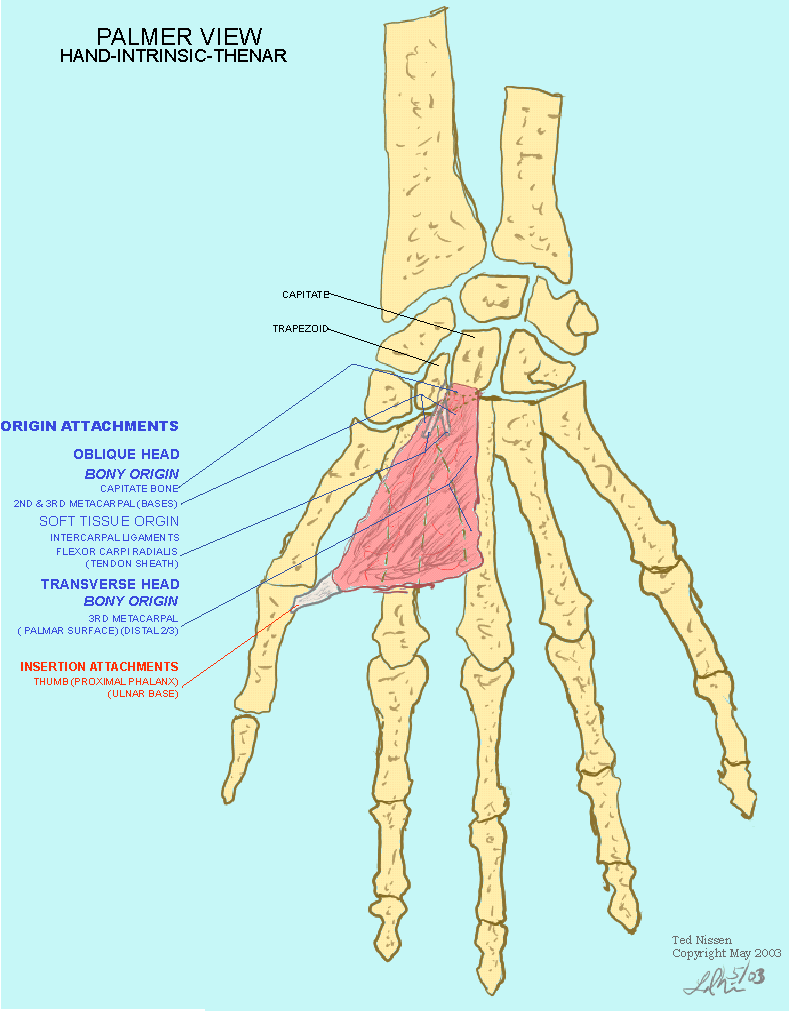
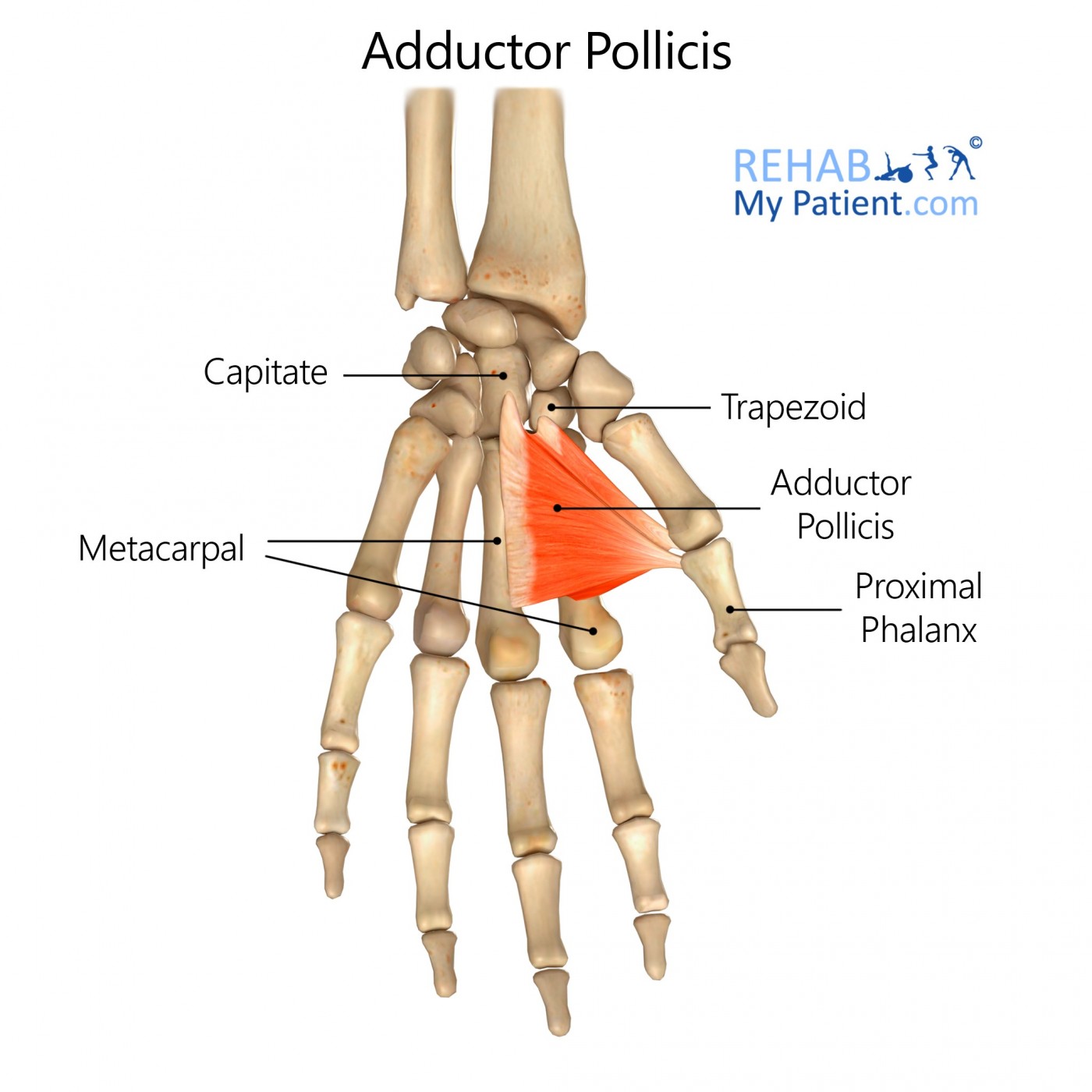
The adductor pollicis muscle is an intrinsic muscle of the hand which lies in the deepest muscular plane of the palm, within the adductor compartment. It is a unique muscle, in that it is triangular shaped with a 2-headed structure. The oblique head originates at the capitate as well as at the bases of the 2nd and 3rd metacarpals, while the.

Adductor pollicis Trigger Point Learn Muscles
Adductor pollicis muscle lies deep to thenar muscles. It has two heads, oblique head and the transverse head. Origin [edit | edit source] Oblique head originates from bases of 2nd-3rd metacarpals; Transverse head originates from the shaft of 3rd metacarpal ; Insertion [edit | edit source] The base of proximal phalanx of thumb on its medial aspect
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13084/F8SGcXD8C3dg3IiauW1Bog_N9fzgyysnd_Musculus_adductor_pollicis_1_copy.png)
Adductor pollicis Origin, insertion and function Kenhub
The Adductor Pollicis is an intrinsic triangular muscle that has two heads: the transverse and oblique. These heads originate from different locations within the hand, with the transverse head beginning at the palmar base of the third metacarpal bone and the oblique head originating from the capitate bone and the palmar bases of the second and third metacarpals.
Origin of oblique head of adductor pollicis Anatomy MCQ
The Adductor Pollicis is a member of the Central Compartment Group of intrinsic muscles of the hand, composed of the: The Adductor Pollicis has two heads: Oblique head and Transverse head. The adductor pollicis attaches from the third metacarpal to the proximal phalanx of the thumb. The oblique head attaches onto the second and third metacarpals.
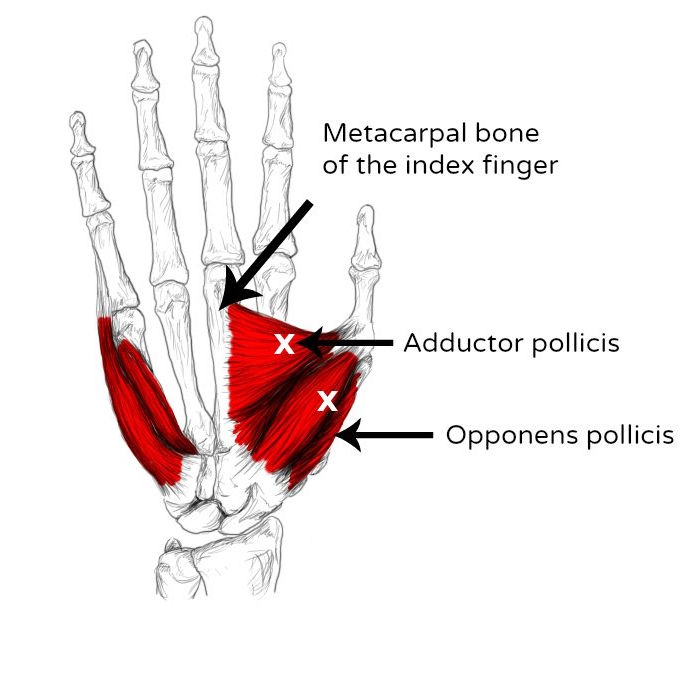
Opponens and adductor pollicis pain & trigger points
Adductor Pollicis is a fleshy, flat, triangular, and fan-shaped muscle deep in the thenar compartment beneath the long flexor tendons and the lumbrical muscles at the center of the palm. It is situated in the palm and plays a vital role in the movement of the thumb. The term "pollicis" refers to the thumb, and "adductor" signifies its.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/de/musculus-abductor-pollicis-brevis/D0DQY2ex5nlOCHu6nCFc5w_lSCPLnc0hPBMyC68gGyOQw_ZSX4oN1kA8_Musculus_abductor_pollicis_brevis_1.png)
Musculus abductor pollicis brevis Anatomie & Funktion Kenhub
Adductor Pollicis. Origin: Oblique head: bases of 2nd and 3rd metacarpals, capitate, and adjacent carpals; Transverse head: anterior surface of body of 3rd metacarpal. Insertion: Medial side of base of proximal phalanx of thumb. Action: Draws 1st metacarpal laterally to oppose thumb toward center of palm and rotates it medially.
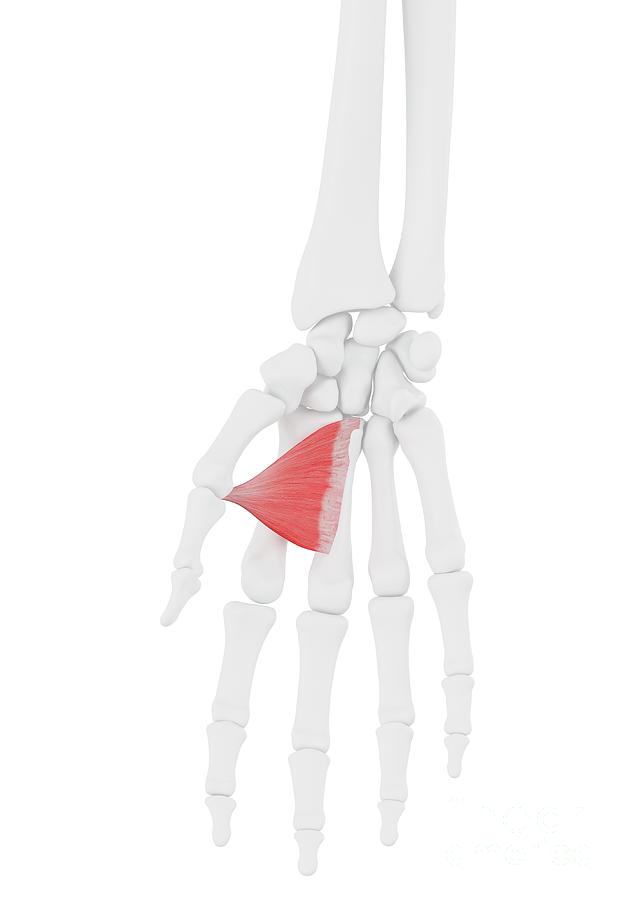
Adductor Pollicis Muscle Photograph by Sebastian Kaulitzki/science Photo Library Fine Art America
Adductor pollicis muscle (Musculus adductor pollicis) Adductor pollicis is a triangular intrinsic muscle of the hand.Although it is found in the thenar region of the hand, the adductor pollicis is the sole muscle of the adductor compartment of the hand, and does not form part of the thenar muscle group, which includes the abductor pollicis, flexor pollicis brevis, and opponens pollicis.

Adductor Pollicis Anatomy Origin, Insertion, Action, Innervation The Wellness Digest
The adductor pollicis is an intrinsic muscle of the hand. It is a triangular shape with two heads. The radial artery passes anteriorly through the space between the two heads to form the deep palmar arch. One head originates from the third metacarpal. The other head originates from the capitate and adjacent areas of second and third metacarpal.

Abductor Pollicis Longus Muscle Overview Human Anatomy Kenhub YouTube
Although the adductor pollicis is not part of the thenar muscle group, it is sometimes described together with the thenar muscles when discussing the movements of the thumb. It is a short and broad, fan-shaped muscle of the palm and arises by the two muscular heads: oblique and transverse.The transverse head originates from the palmar base of metacarpal bone 3, while the oblique head arises.
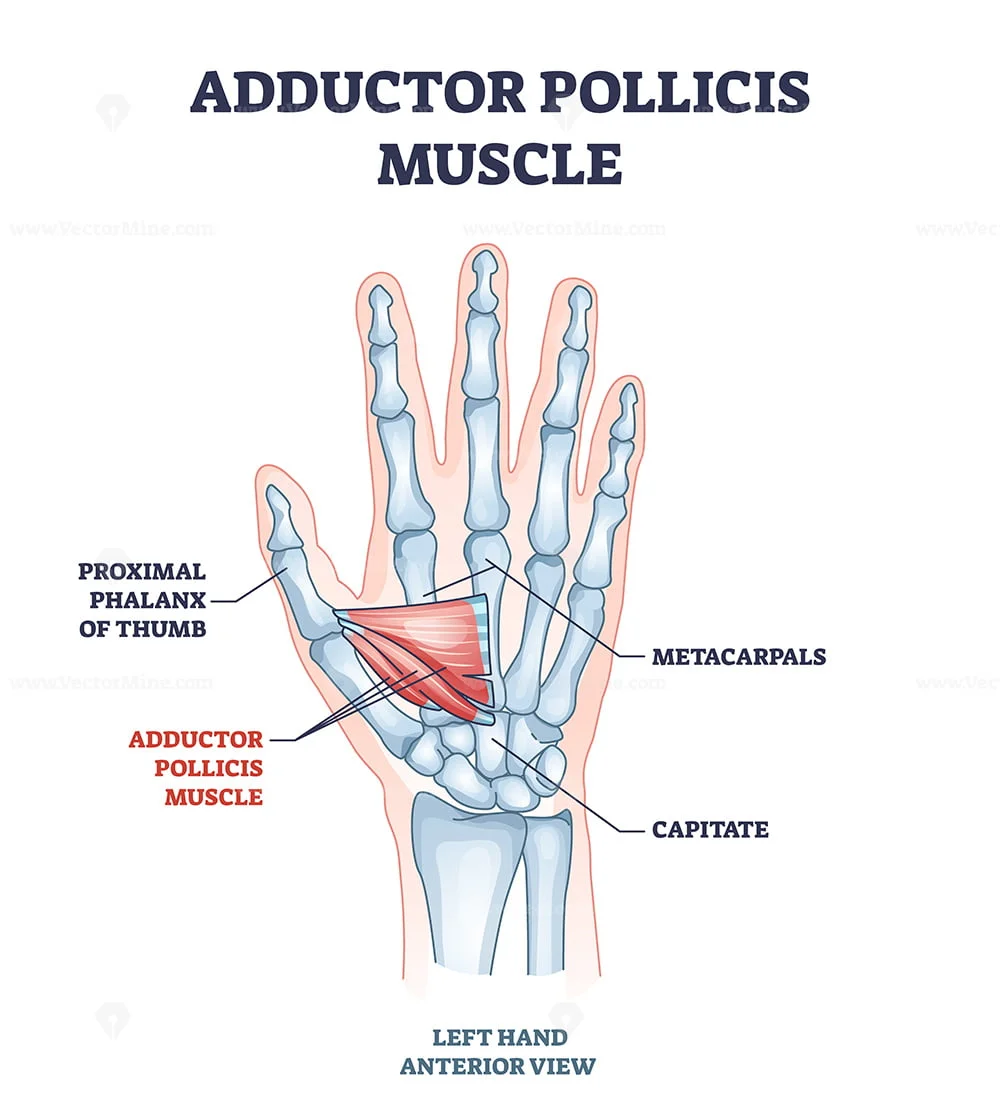
Adductor pollicis muscle with hand or palm skeletal system outline diagram VectorMine
In human anatomy, the adductor pollicis muscle is a muscle in the hand that functions to adduct the thumb. It has two heads: transverse and oblique.

Abductor pollicis brevis muscle Wikiwand
In human anatomy, the adductor pollicis muscle is a muscle in the hand that functions to adduct the thumb. It has two heads: transverse and oblique. It is a fleshy, flat, triangular, and fan-shaped muscle deep in the thenar compartment beneath the long flexor tendons and the lumbrical muscles at the center of the palm. It overlies the metacarpal bones and the interosseous muscles.