
Fluorine Electron Dot Diagram
1 Ry = e4me 8ϵ2 0h2 = 2.18 × 10 − 18 J. and this simplifies the allowed energies predicted by the Bohr model (Equation 7.4.11) as. En = − (2.18 × 10 − 18)Z2 n2 J = − Z2 n2 Ry. Hence, the energy of the electron in an atom also is quantized. Equation 7.4.12 gives the energies of the electronic states of the hydrogen atom.
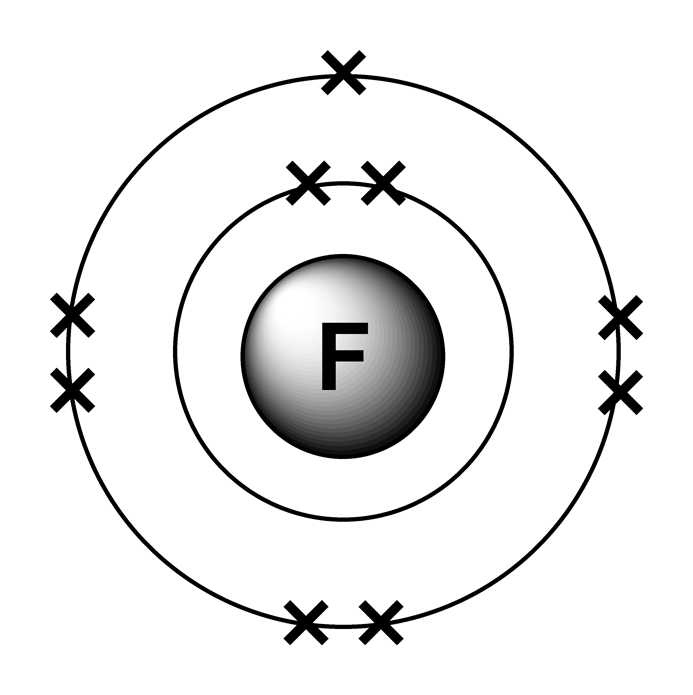
Fluorine Electron Dot Structure My XXX Hot Girl
For more information and resources, please visit: https://sites.google.com/tdsb.on.ca/htc-meyer/home/9-Science/9-chemistry

What is the Bohr model for fluorine? Quizlet
Bohr diagram is very interesting and easy to draw. Here, we will draw the Bohr diagram of the Fluorine atom with some simple steps. Steps to draw the Bohr Model of Fluorine atom 1. Find the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in the Fluorine atom
13+ Diagram Of Fluorine ArmaanDallas
In this video we'll look at the atomic structure and Bohr model for the Fluorine atom (F). We'll use a Bohr diagram to visually represent where the electrons.

Bohr Model Of Fluorine
The electron configuration and the orbital diagram are: Following hydrogen is the noble gas helium, which has an atomic number of 2. The helium atom contains two protons and two electrons. The first electron has the same four quantum numbers as the hydrogen atom electron ( n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = +12 m s = + 1 2 ).

Fluorine Atom Diagram
In order to make a Bohr diagram, you need to know the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons the element has. In this section, we'll show a sample Bohr diagram for hydrogen. H —Hydrogen 1 proton 1 electron 0 neutrons You can see the principles outlined in the section above at work in the Bohr model for the hydrogen atom.
Fluorine Bohr Diagram
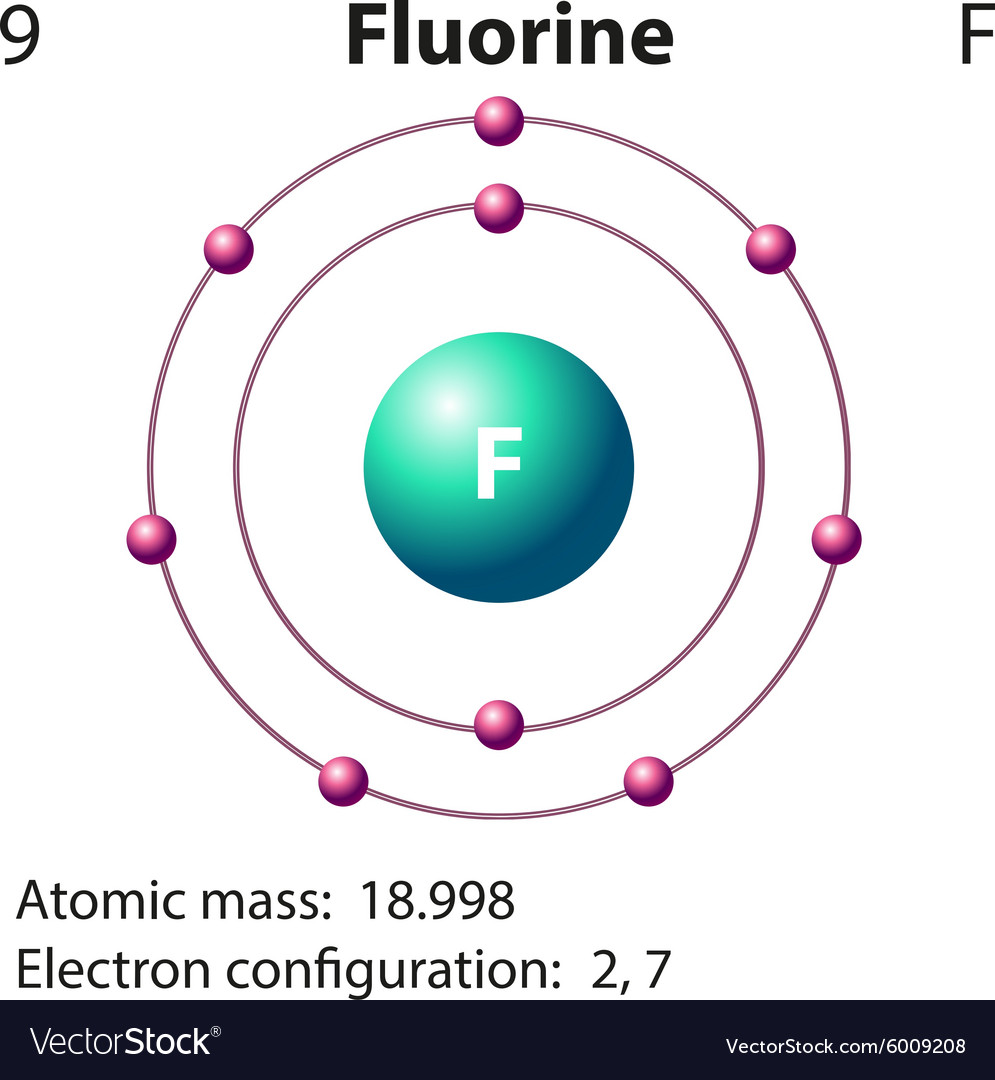
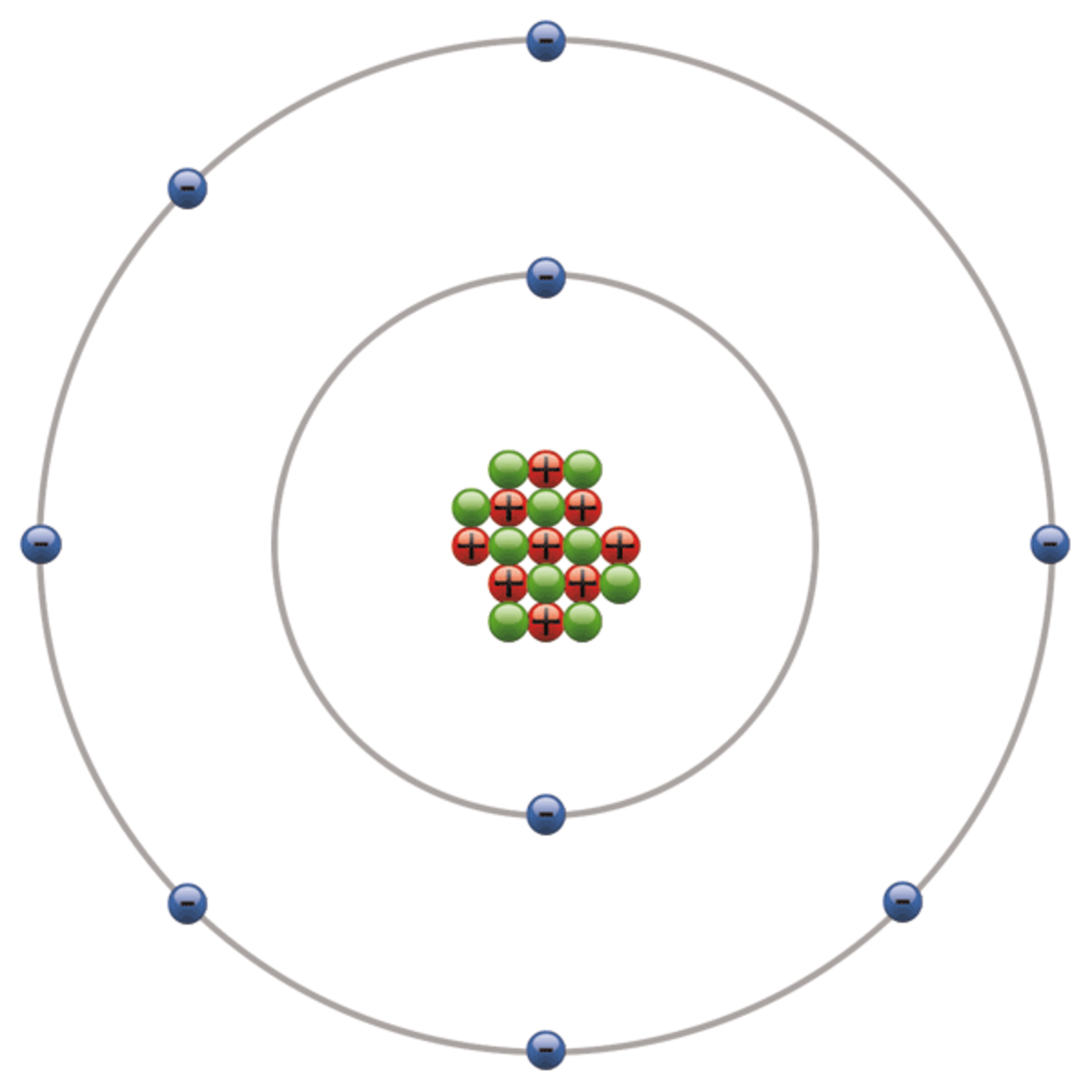
This is the Bohr-Rutherford Diagram for Fluorine (Atomic Number 9). Fluorine is the ninth element of the Periodic Table. As shown, Fluorine has nine protons (i.e., 9p) and ten neutrons (i.e., 10n). Thus, its Atomic Mass is 19. Fluorine also has nine total electrons -- two electrons in Orbit 1, seven electrons in Orbit 2.

Fluorine Bohr Diagram
Fluorine is a Group 7 element, on the Periodic Table, with an atomic number of 9. About Fluorine Molecular Structure Fluorine has the chemical formula F 2. Atomic Structure Fluorine as 9 protons and 10 neutrons in its nucleus giving it an Atomic Number of 9 and an atomic mass of 19. An atom of Fluorine is missing one electron from having a full.

Fluorine Atom Diagram
Podcasts Produced by The Naked Scientists. Periodic Table of Videos Created by video journalist Brady Haran working with chemists at The University of Nottingham. Element Fluorine (F), Group 17, Atomic Number 9, p-block, Mass 18.998. Sources, facts, uses, scarcity (SRI), podcasts, alchemical symbols, videos and images.

Fluorine Atom Bohr Model With Proton Neutron And Electron Stock Photo
Name: Fluorine Symbol: F Atomic Number: 9 Atomic Mass: 18.998404 amu Melting Point:-219.62 °C (53.530006 K, -363.31598 °F) Boiling Point:-188.14 °C (85.01 K, -306.652 °F) Number of Protons/Electrons: 9 Number of Neutrons: 10 Classification: Halogen Crystal Structure: Cubic Density @ 293 K: 1.696 g/cm 3 Color: Greenish Atomic Structure
Fluorine The Most Reactive Element in Periodic Table Owlcation
On the far left of Figure 3.6.1 3.6. 1 are the highest energy electromagnetic waves. These are called gamma rays and can be quite dangerous, in large numbers, to living systems. The next lower energy form of electromagnetic waves are called x-rays. Most of you are familiar with the penetration abilities of these waves.

Fluorine Diagram
Composition and Structure: Fluorine (F) is the first element in the Halogen group (group 17) in the periodic table. It has an atomic number of 9, meaning that it consists of 9 protons and 9 electrons. Since its atomic weight is 18.998 grams, it can be assumed that there are 10 neutrons within the nucleus of the atom.
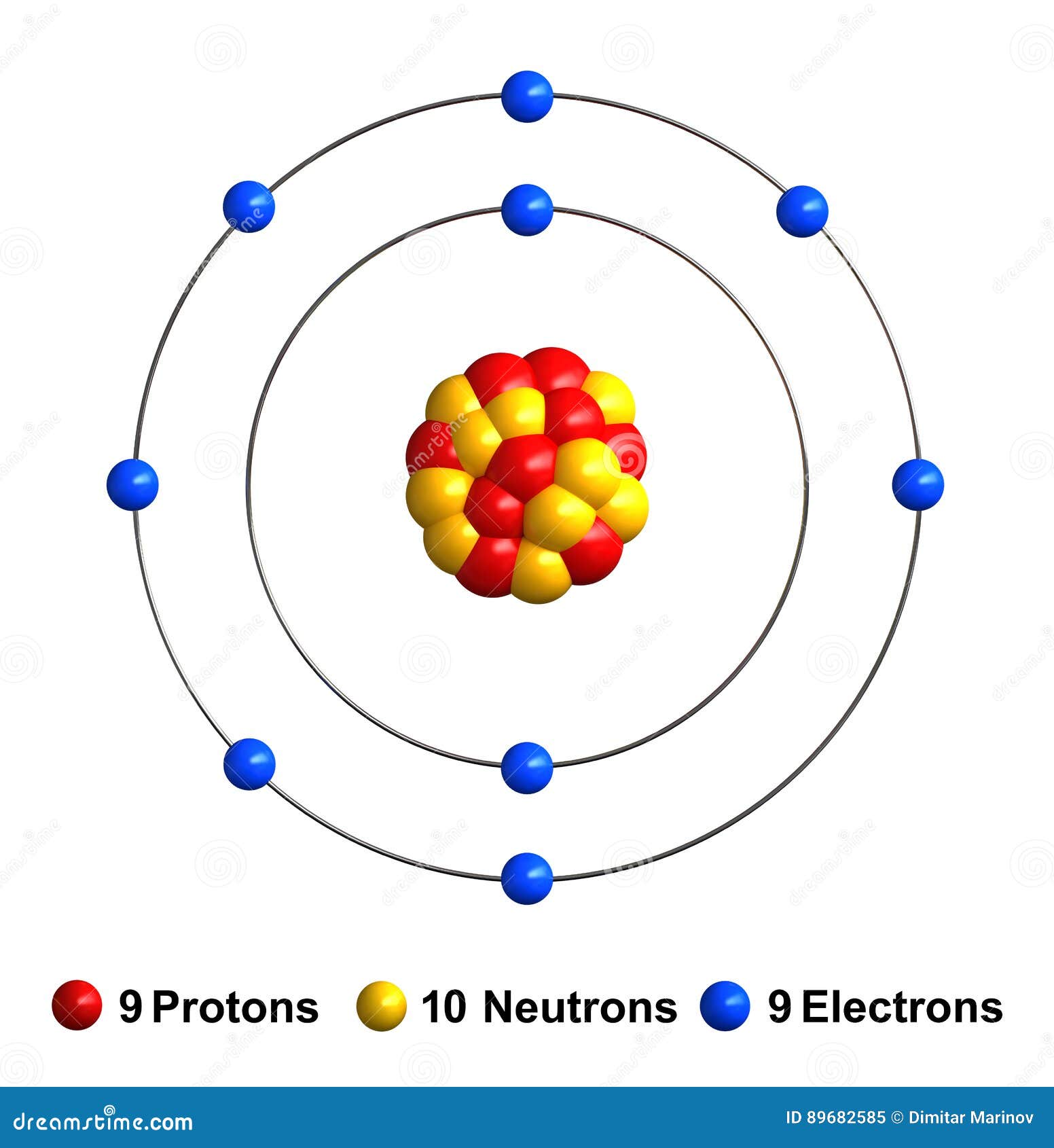
Fluorine stock illustration. Illustration of protons 89682585
December 14, 2023 by Deep The information on this page is fact-checked. Fluorine Bohr model In the fluorine Bohr model, the nucleus holds 9 protons and 10 neutrons. Encircling this nucleus are two electron shells, carrying a total of 9 electrons. To draw the fluorine Bohr model, note the 9 protons, 10 neutrons, and 9 electrons.

Fileelectronformula N2svg Wikimedia Commons
By convention, elements are organized in the periodic table, a structure that captures important patterns in their behavior.Devised by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev (1834-1907) in 1869, the table places elements into columns—groups—and rows—periods—that share certain properties.These properties determine an element's physical state at room temperature—gas, solid, or liquid.
Fluorine Bohr Diagram
Key points Bohr's model of hydrogen is based on the nonclassical assumption that electrons travel in specific shells, or orbits, around the nucleus. Bohr's model calculated the following energies for an electron in the shell, n : E ( n) = − 1 n 2 ⋅ 13.6 eV
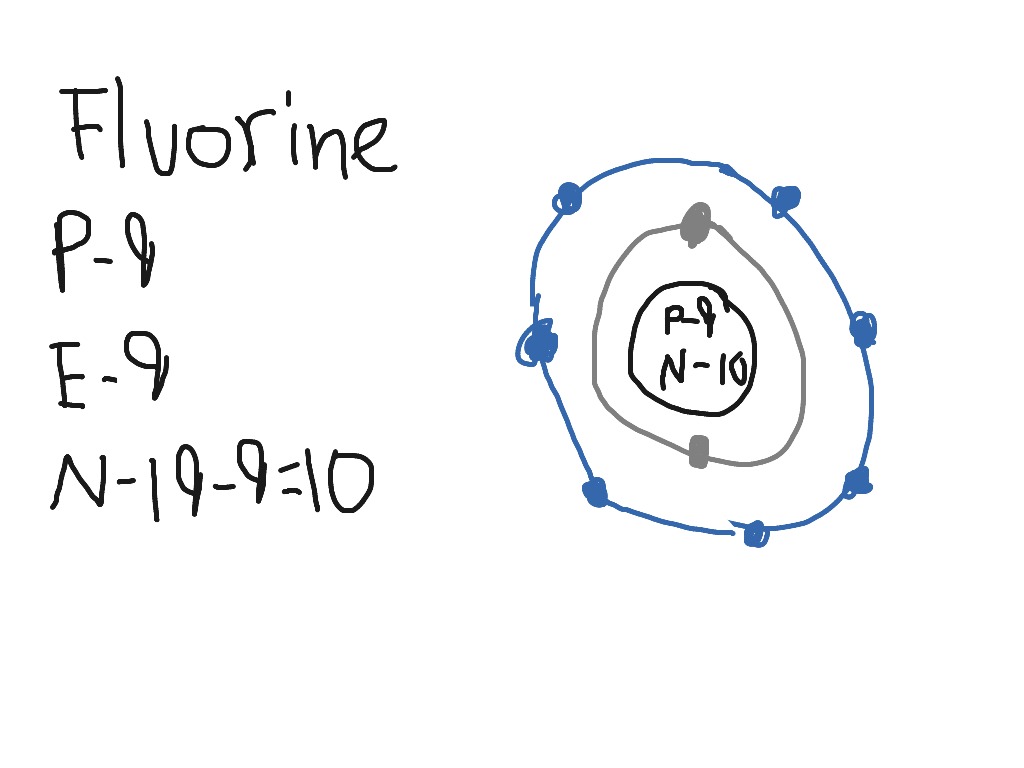
Bohr Diagram For Fluorine General Wiring Diagram
Bohr diagrams for hydrogen, helium, lithium, carbon, fluorine, neon, sodium, silicon, chlorine, and argon. Bohr diagrams indicate how many electrons fill each principal shell. Group 18 elements (helium, neon, and argon are shown in Figure 2) have a full outer, or valence, shell. A full valence shell is the most stable electron configuration.