Nitrogen Cycle Introduction, Stages and its Process
This type of cycle of atoms between living and non-living things is known as a biogeochemical cycle. All of the atoms that are building blocks of living things are a part of biogeochemical cycles. The most common of these are the carbon and nitrogen cycles. Tiny atoms of carbon and nitrogen are able to move around the planet through these cycles.
Nitrogen cycle Steps of Nitrogen cycle Online Biology Notes
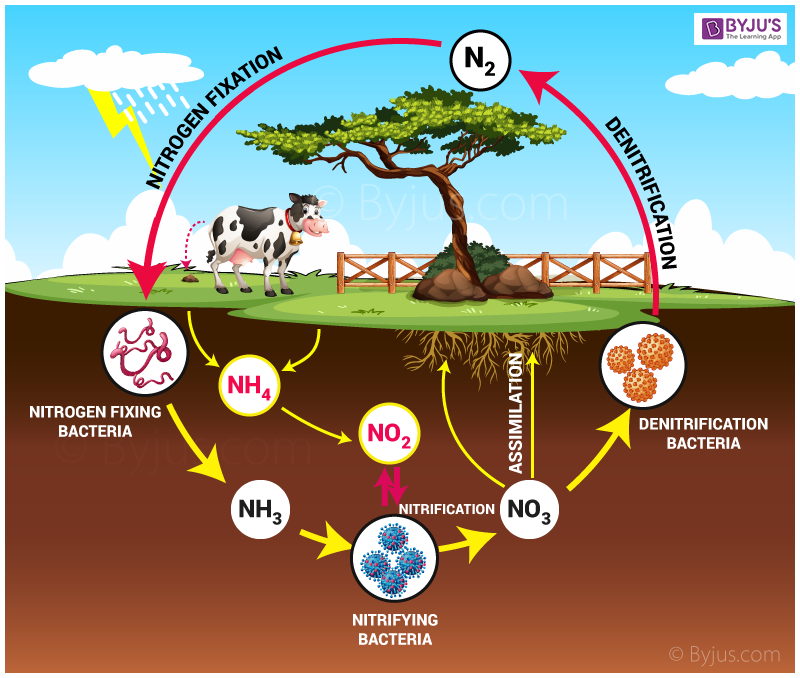
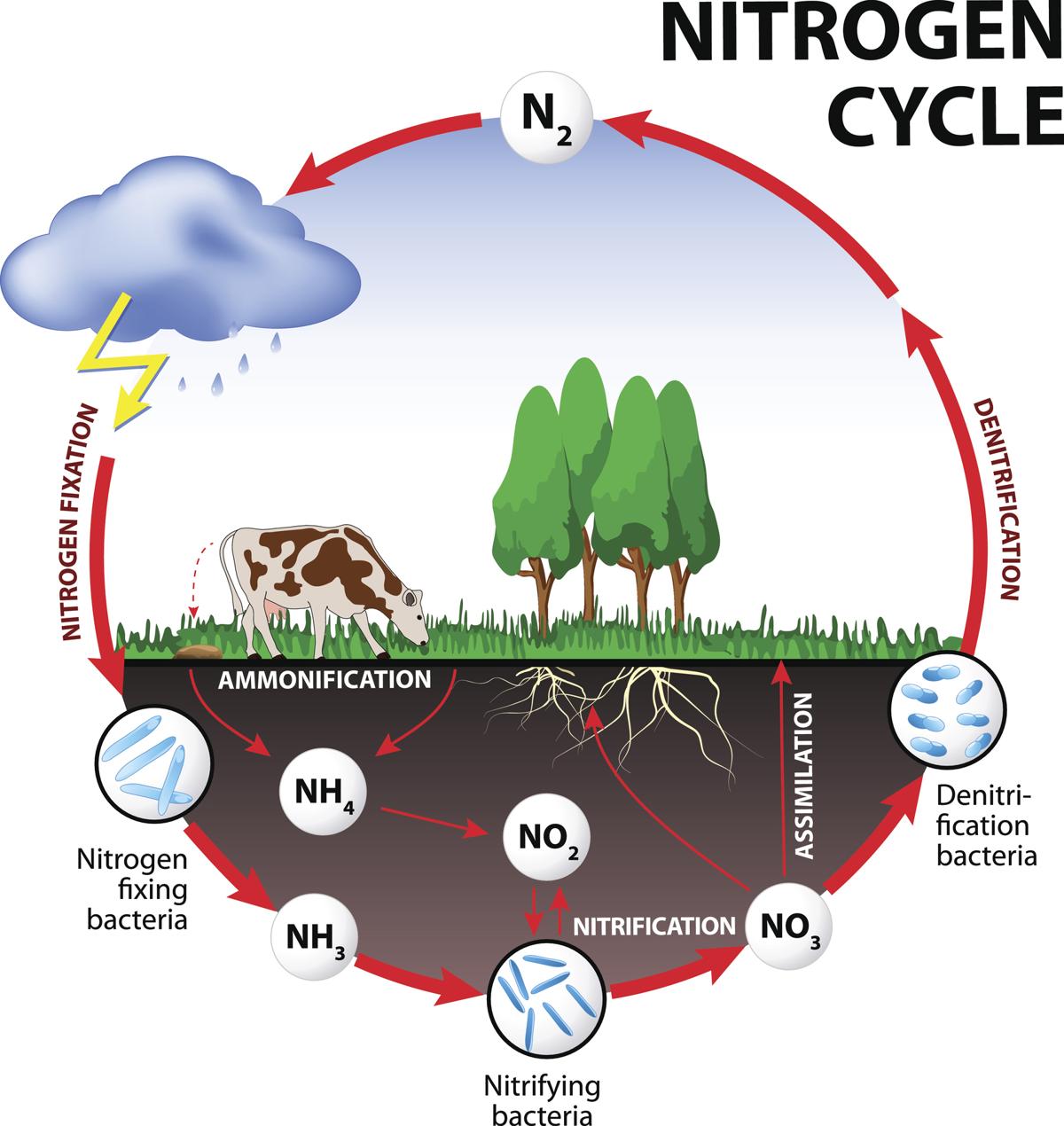
. Nitrogen exists in the atmosphere as N 2 gas. In nitrogen fixation, bacteria convert N 2 into ammonia, a form of nitrogen usable by plants. When animals eat the plants, they acquire usable nitrogen compounds. Nitrogen is a common limiting nutrient in nature, and agriculture.
Explain Different Steps of Nitrogen Cycle
What to keep in mind? Plants do not have the ability to use atmospheric nitrogen. They need the help of nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Nitrogen depletion in soils is remedied by planting crops like beans and alfalfa. Nitrogen can be fixed through man-made processes such as the creation of nitrogen and ammonia fertilizers. (2, 3, and 4)

Understanding the Nitrogen Cycle Beginners Education AlgaeBarn
Share it! Similar to other biogeochemical cycles, the nitrogen cycle is essential for regulating the concentration of nitrogen in the atmosphere. Read on to know more about this cycle through the diagram given below, which will help you in understanding the sequence of steps involved in this cycle.

The Nitrogen Cycle Explained Fountains 2 Go
The nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates among atmospheric, terrestrial, and marine ecosystems. The conversion of nitrogen can be carried out through both biological and physical processes.

Nitrogen Cycle Definition, Steps, Process, Significance
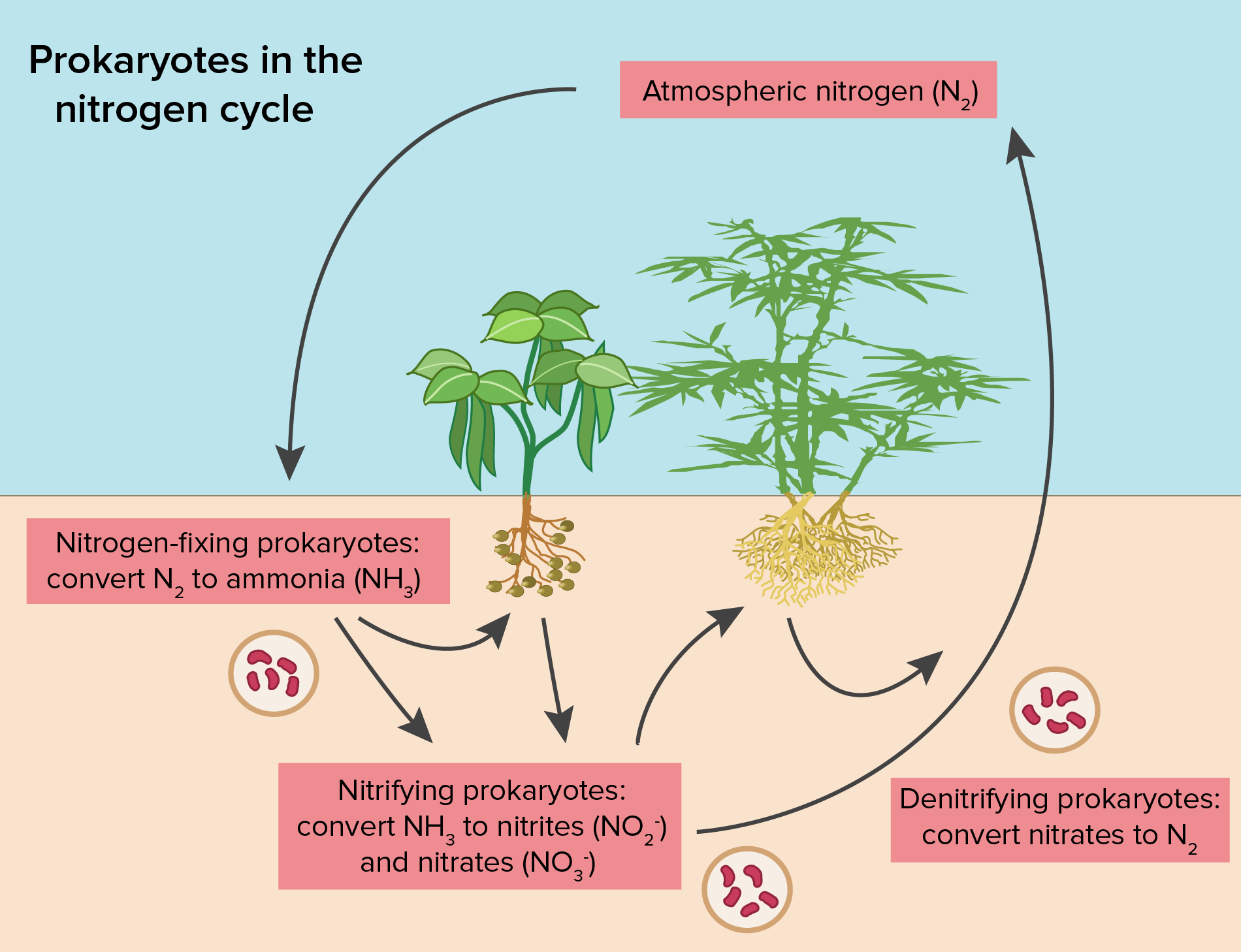
Plants must secure their nitrogen in "fixed" form, i.e., incorporated in compounds such as: nitrate ions (NO 3 − ), ammonium ions (NH 4 +) and urea (NH 2) 2 CO. Animals secure their nitrogen (and all other) compounds from plants (or animals that have fed on plants). Figure 17.2.2.1 Nitrogen cycle. Four processes participate in the cycling of.

Nitrogen Cycle Facts for Kids (Explained!) Education site
The series of processes by which nitrogen and its different forms are circulated and interconverted in nature with the help of living organisms is called the nitrogen cycle. It shows the path that nitrogen follows through the biogeochemical cycle using its storage reservoirs, such as the atmosphere, living organisms, and soil.

Nitrogen Cycle QCE Biology Revision
The nitrogen cycle is a biogeochemical cycle that converts nitrogen into various forms throughout the ecosystem. Nitrogen is an essential element for life that organisms use in the synthesis of amino acids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Yet, while the atmosphere is rich in nitrogen (about 78%), this nitrogen (N 2) is largely inaccessible to.

[DIAGRAM] Simple Diagram Of The Nitrogen Cycle
Biologically: Nitrogen gas (N 2) diffuses into the soil from the atmosphere, and species of bacteria convert this nitrogen to ammonium ions (NH 4+ ), which can be used by plants. Legumes (such as clover and lupins) are often grown by farmers because they have nodules on their roots that contain nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
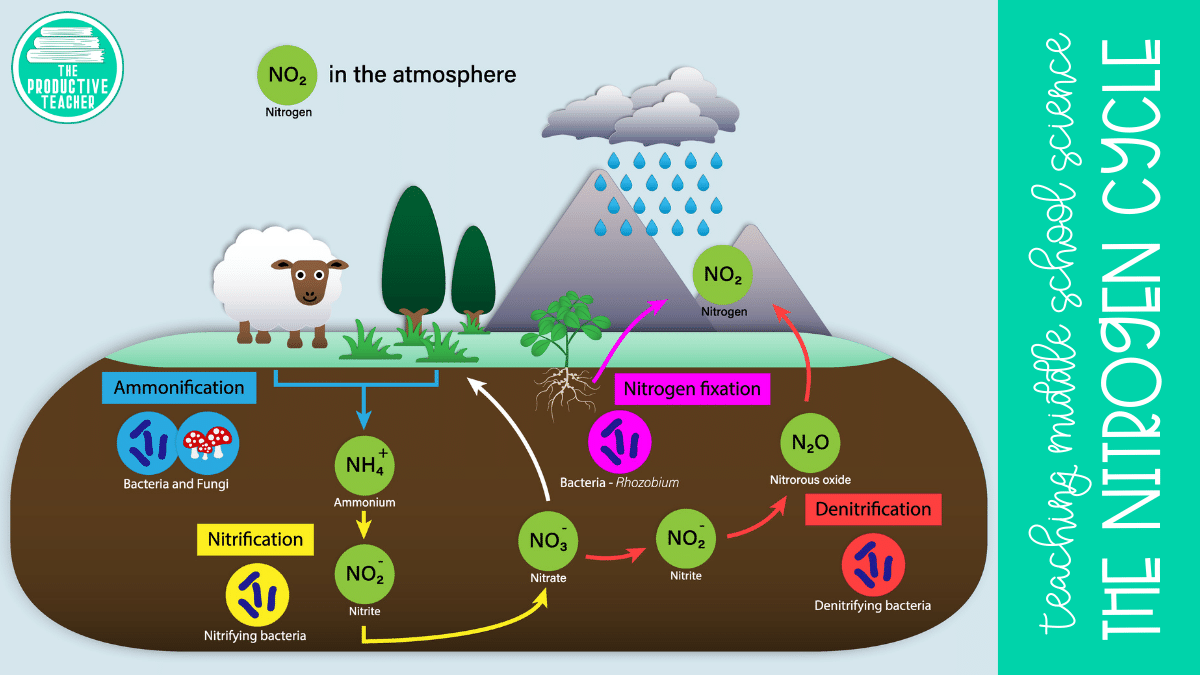
How to Remember the Steps of the Nitrogen Cycle The Productive Teacher
Diagram of the nitrogen cycle Processes in the Nitrogen Cycle Fixation - Fixation is the first step in the process of making nitrogen usable by plants. Here bacteria change nitrogen into ammonium. Nitrification - This is the process by which ammonium gets changed into nitrates by bacteria. Nitrates are what the plants can then absorb.

Simplified nitrogen cycle (after [64]).... Download Scientific Diagram
Nitrogen Cycle. The N cycle illustrates how N from manure, fertilizers and plants moves through the soil to crops, water and the air. Understanding the N cycle will help you make the best use of manure and fertilizers to meet crop needs while safeguarding the environment. In general, the N cycle processes of fixation, mineralization and.

Understanding the Nitrogen Cycle Beginners Education AlgaeBarn
Nitrogen Cycle is a biogeochemical process through which nitrogen is converted into many forms, consecutively passing from the atmosphere to the soil to organism and back into the atmosphere. It involves several processes such as nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, decay and putrefaction.
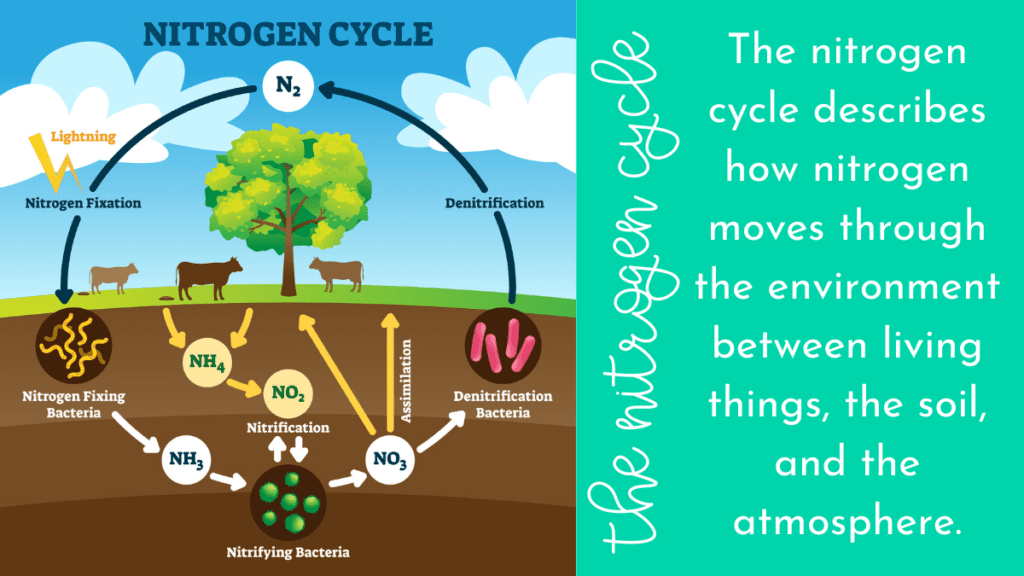
How to Remember the Steps of the Nitrogen Cycle The Productive Teacher
The nitrogen cycle refers to the cycle of nitrogen atoms through the living and non-living systems of Earth. The nitrogen cycle is vital for life on Earth. Through the cycle, atmospheric nitrogen is converted to a form which plants can incorporate into new proteins. Nitrogen Cycle Explained

Diagram Of Nitrogen Cycle
Nitrogen, the most abundant element in our atmosphere, is crucial to life. Nitrogen is found in soils and plants, in the water we drink, and in the air we breathe. It is also essential to life: a key building block of DNA, which determines our genetics, is essential to plant growth, and therefore necessary for the food we grow.
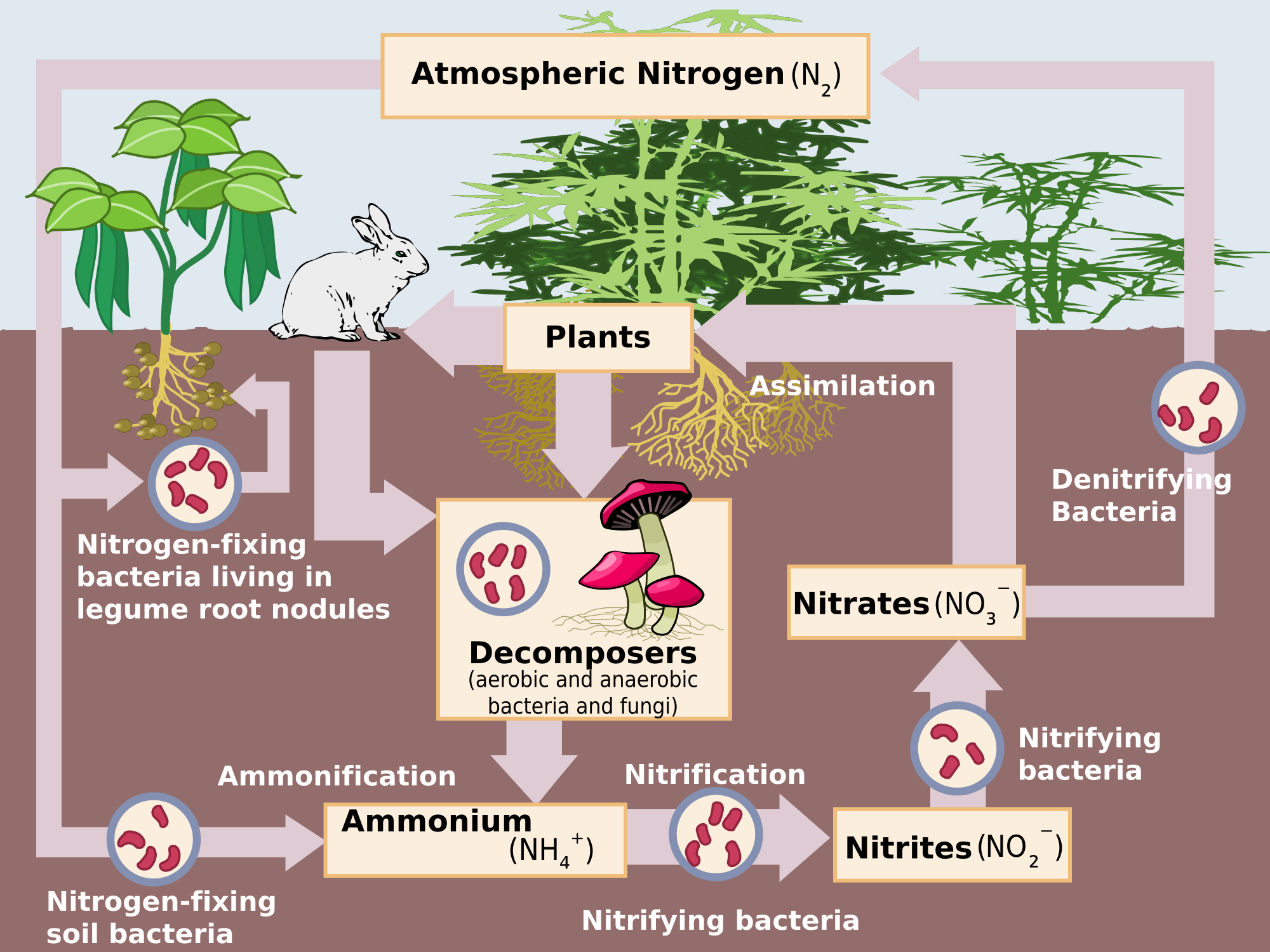
How does nitrogen cycle through the biosphere? Socratic
Nitrogen cycle - Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Nitrogen cycle Nitrogen cycle The nitrogen cycle is the way that nitrogen in nature is changed into many different forms that are used by living organism [s]. Air is about 78% nitrogen. Nitrogen chemicals are needed for life. Nitrogen is a necessary part of proteins, DNA, and RNA.
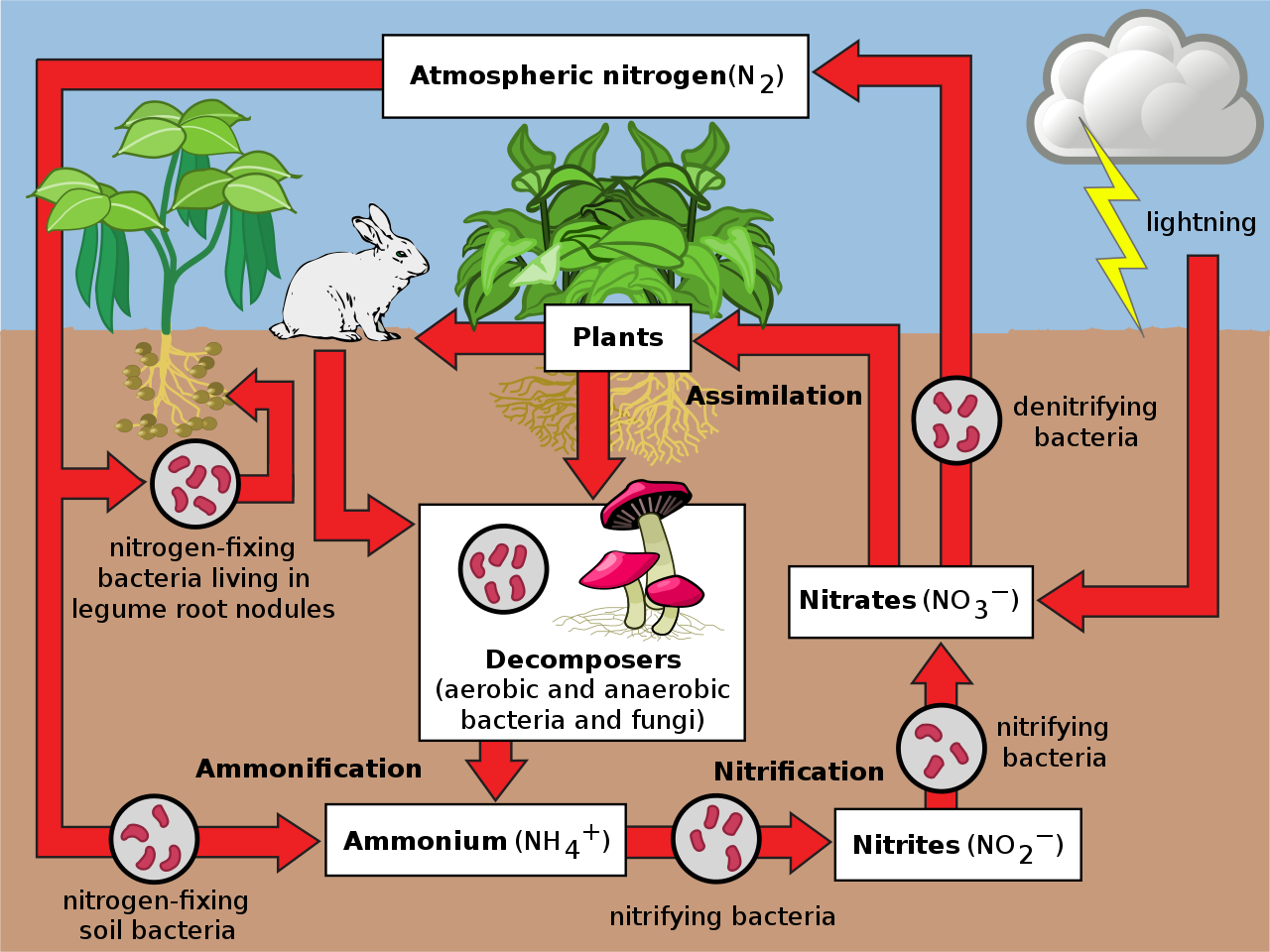
What is Nitrogen Cycle? Diagram, Stages, Importance Tutoroot
Nitrogen cycle, circulation of nitrogen in various forms through nature. Nitrogen, a component of proteins and nucleic acids, is essential to life on Earth. Although 78 percent of the atmosphere is nitrogen gas, this gas is unusable by most organisms until it is made available by a series of microbial transformations.