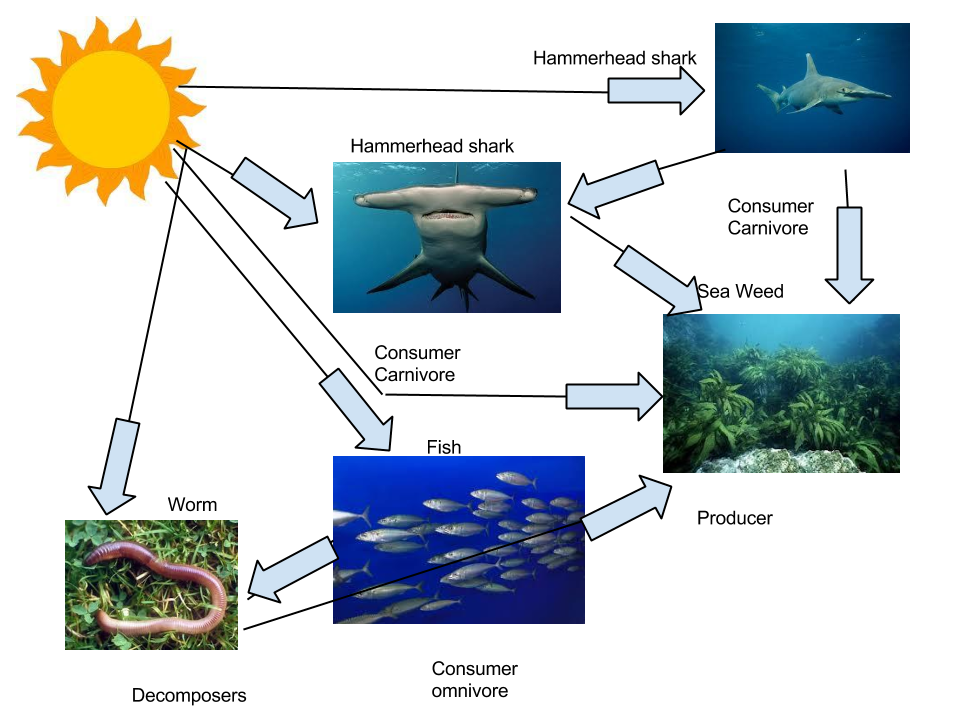
Food web Hammerhead Shark
Marine food webs. Resource. Add to collection. Feeding relationships are often shown as simple food chains - in reality, these relationships are much more complex, and the term 'food web' more accurately shows the links between producers, consumers and decomposers. A food web diagram illustrates 'what eats what' in a particular habitat.

Why We Need Sharks, Maybe Even More Than Trees
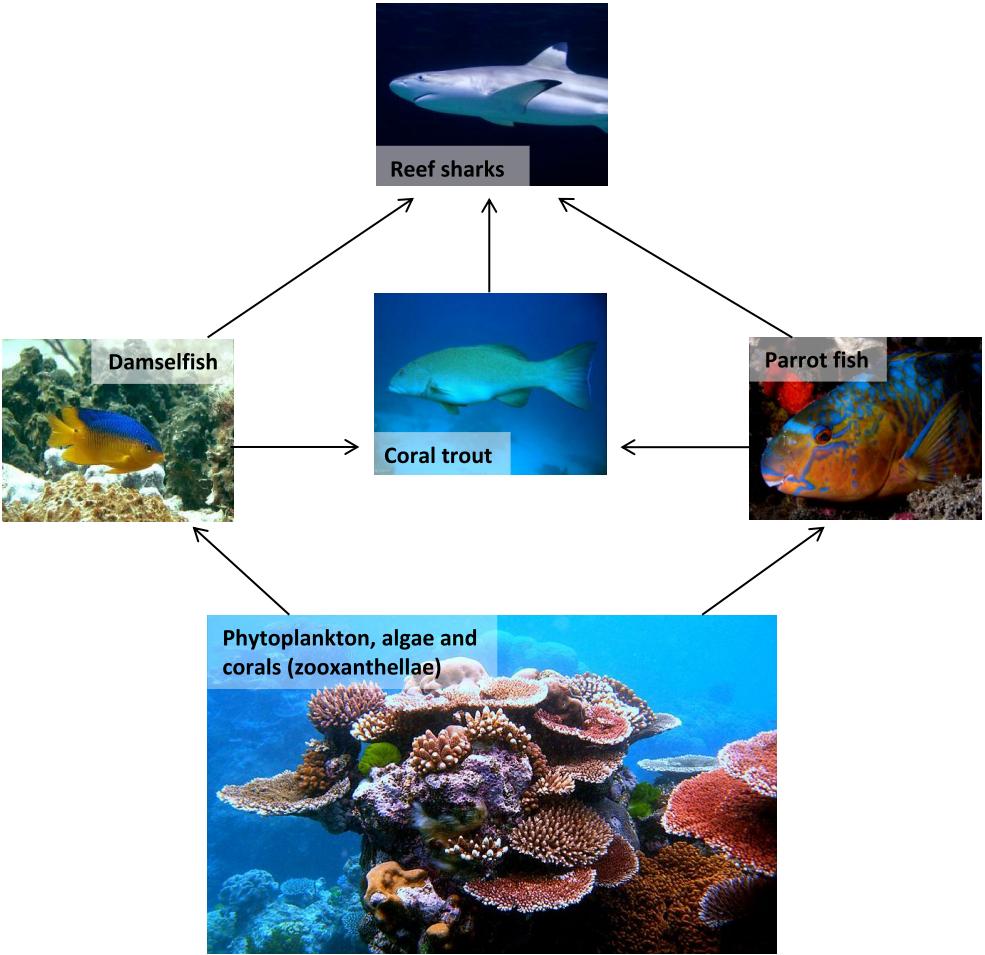
Three food chains (a-c) can be created from the food web represented in Figure 16-9. Food webs are important because they show the direct relationships between organisms; however, they also illustrate the indirect relationships that organisms have with each other. Let's look at an example from the Figure 16-9 food web. Sharks prey on parrotfish.
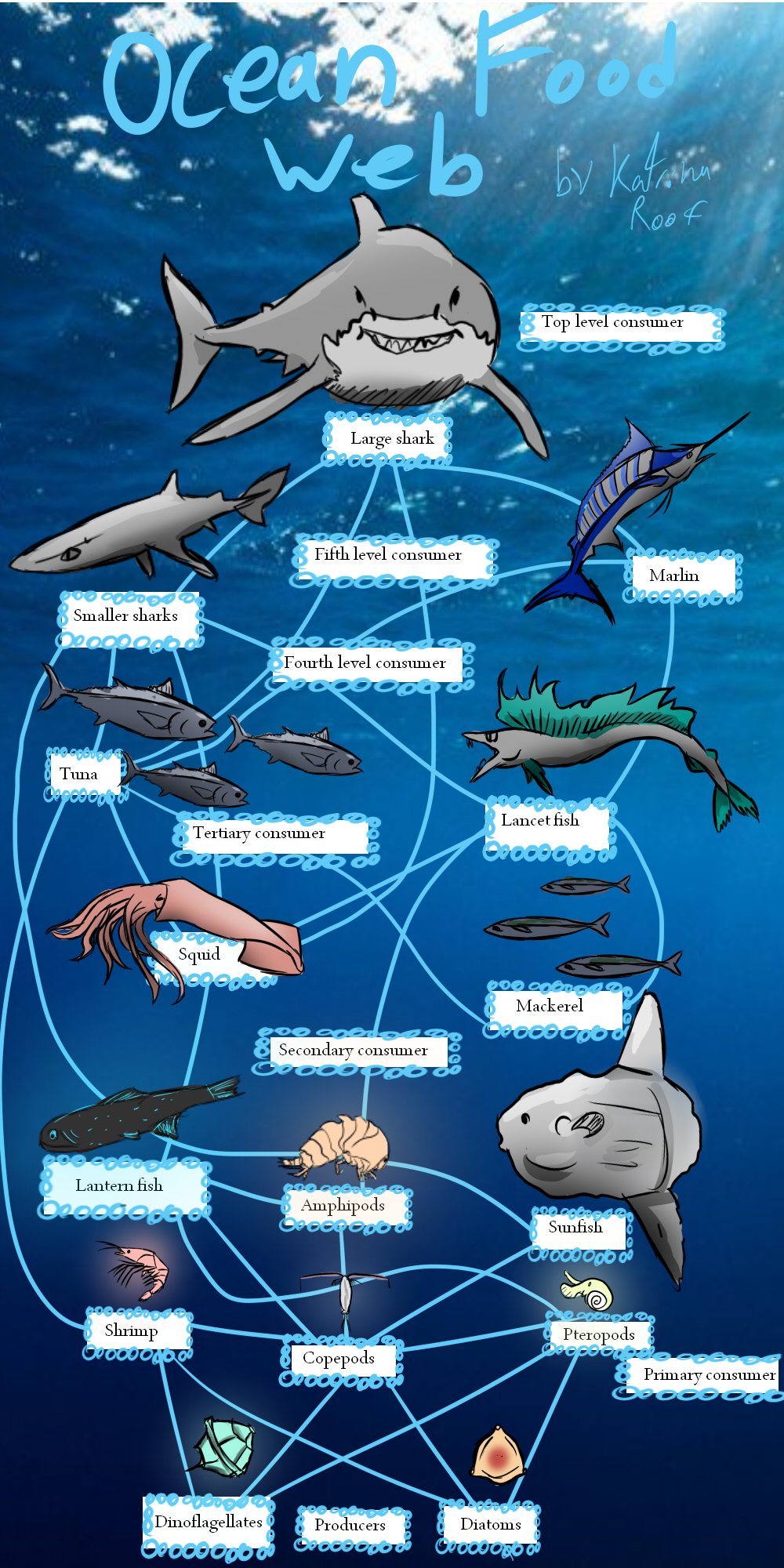
BOI's ocean food web. by Sketchylicious66 on DeviantArt
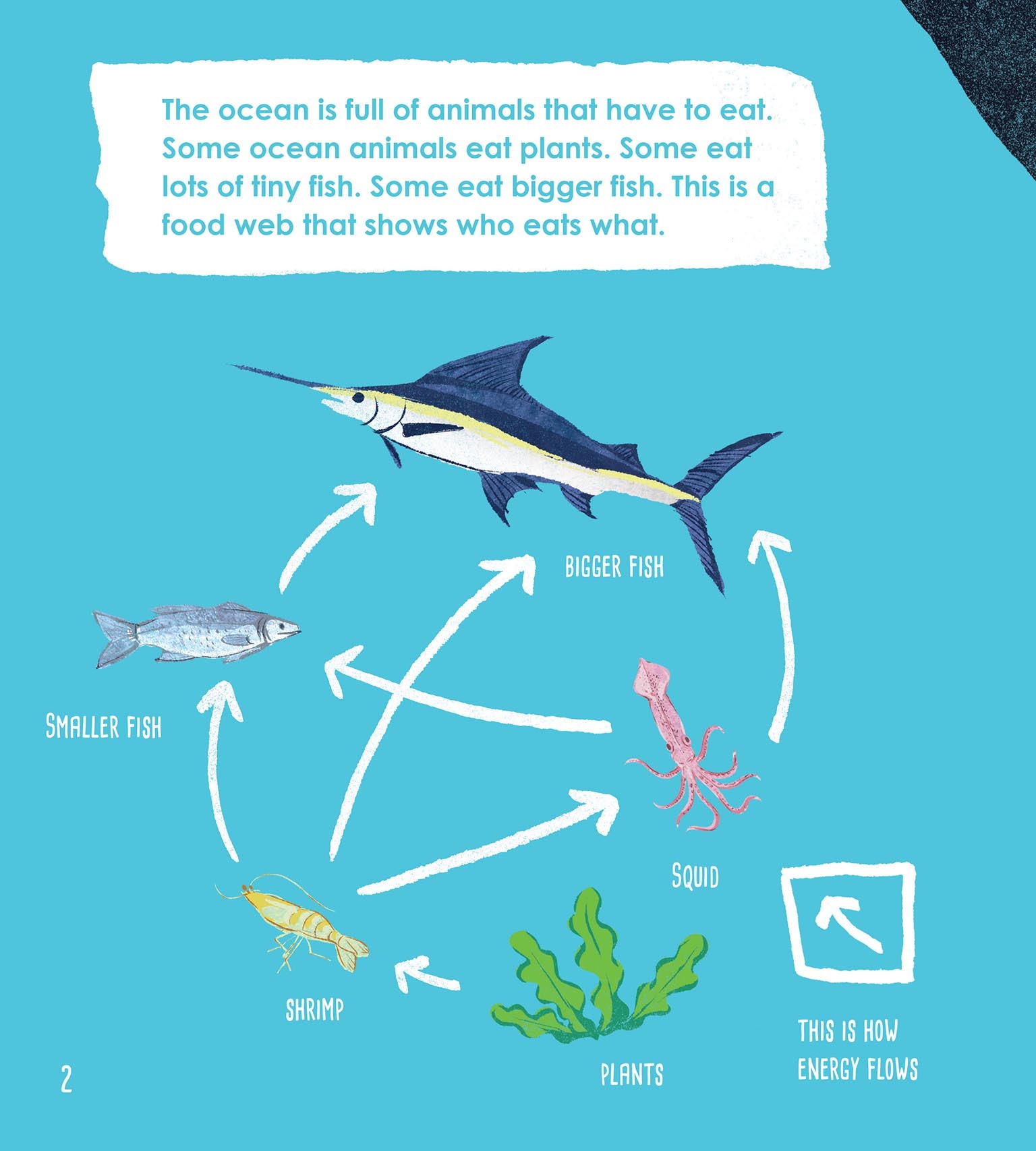
A food web consists of all the food chains in a single ecosystem.Each living thing in an ecosystem is part of multiple food chains.Each food chain is one possible path that energy and nutrients may take as they move through the ecosystem.All of the interconnected and overlapping food chains in an ecosystem make up a food web. Trophic Levels Organisms in food webs are grouped into categories.

Biology Review Jeopardy Template
On the other hand, a food web is a set of food chains that are interconnected. It is based on the same principles, but it provides a much more complex explanation of the movement of energy and matter.. In this group we can find animals of the marine ecosystem food web such as orcas, sharks and even certain species of tuna. Although relevant,.
Samoa Joins The List of Growing Shark Sanctuaries Diving Info
Here's how it works: when the tide rises, sharks make hunting raids into the shallow lagoons. The fish stop eating and hide instead. But during low tide, the predators are isolated in deeper.
Ace Run in the PNW Surviving the Ocean Food Chain
Oceanic sharks appear to get most of their food from food webs in the red shaded regions. Clive Trueman, Author provided. These key differences in the way in which sharks feed could be important.
taxo4254 Carcharhinus melanopterus
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another. Let's look at the parts of a typical food chain, starting from the bottom—the producers—and moving upward. At the base of the food chain lie the primary producers.

Endangered whale sharks strain fish out of the water using huge mouths
As apex predators, tiger sharks and other shark species play a critical role in maintaining the health of ocean ecosystems.But shark populations are decreasi.

icy.tools Digi Sharks NFT tracking & history
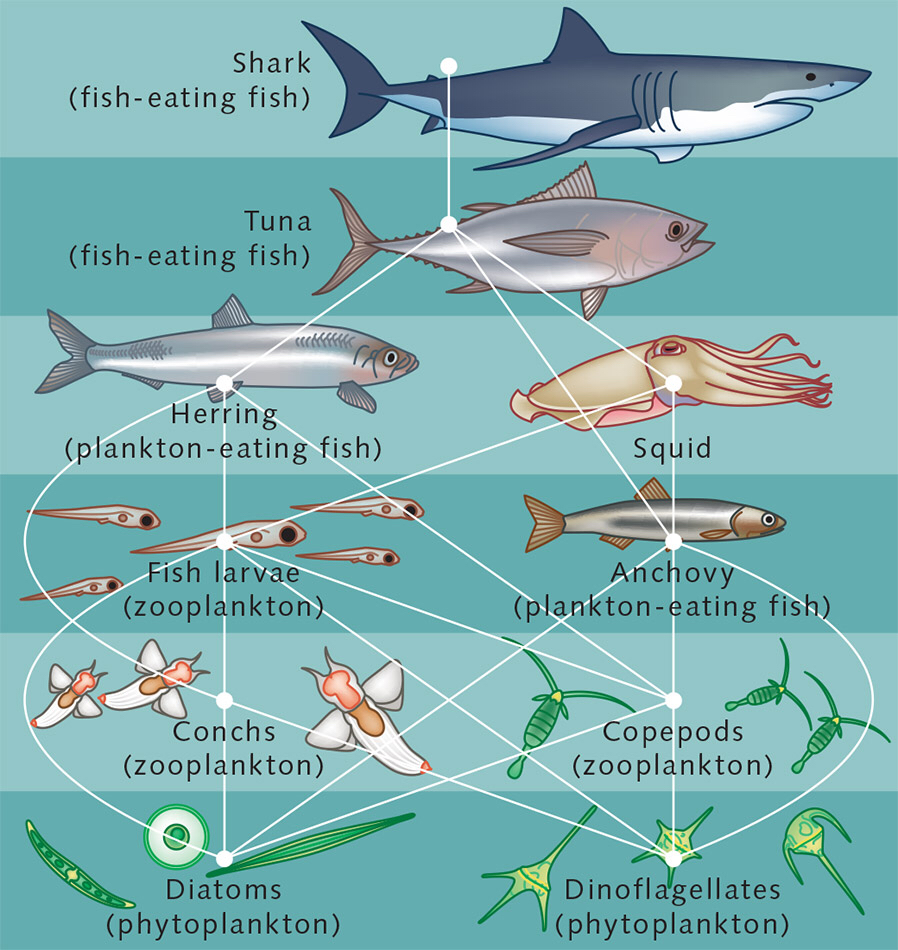
Aquatic food webs. Food webs describe who eats whom in an ecological community. Made of interconnected food chains, food webs help us understand how changes to ecosystems — say, removing a top predator or adding nutrients — affect many different species, both directly and indirectly. Phytoplankton and algae form the bases of aquatic food webs.

Whale Shark, Rhincodon Typus Free Stock Photo Public Domain Pictures
Sharks are carnivores, so they get energy by eating other animals. Predators like sharks help keep prey populations balanced. If a prey population gets too big, they might deplete their own food source. Food webs can show us how everything is connected. Materials. 1 clothes hanger (or a straight rod, like a chopstick or a skewer) Crayons, or.

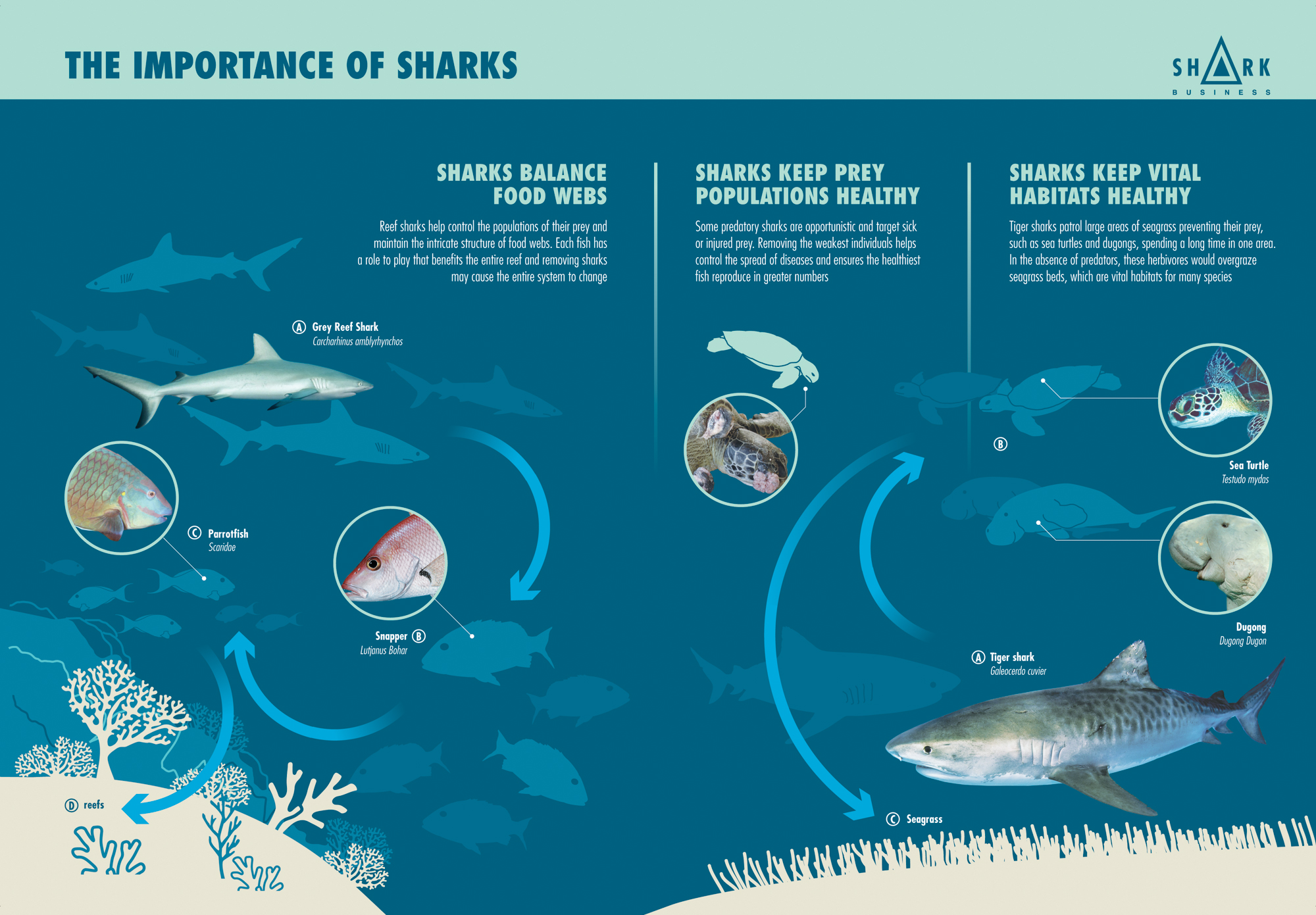
Why are sharks important ? SOSF D'Arros Research Centre
And that's bad news for the creatures even lower on the food web. Along the East Coast of the United States, only sharks that are at least 2 meters (6.6 feet) long are tough enough to eat a lot of the medium-size sharks, rays, and skates living in those waters. Eleven large shark species in the region fit into that category.
Top of the Ocean Food Web Orcas & Great White Sharks by Matt Reher
February 22, 2021. Written by Liz Thompson. Shark populations are dwindling worldwide, and scientists are concerned that the decline could trigger a cascade of impacts that hurt coral reefs. But a new paper published in Ecology suggests that the effects of shark losses are unlikely to reverberate throughout the marine food web.
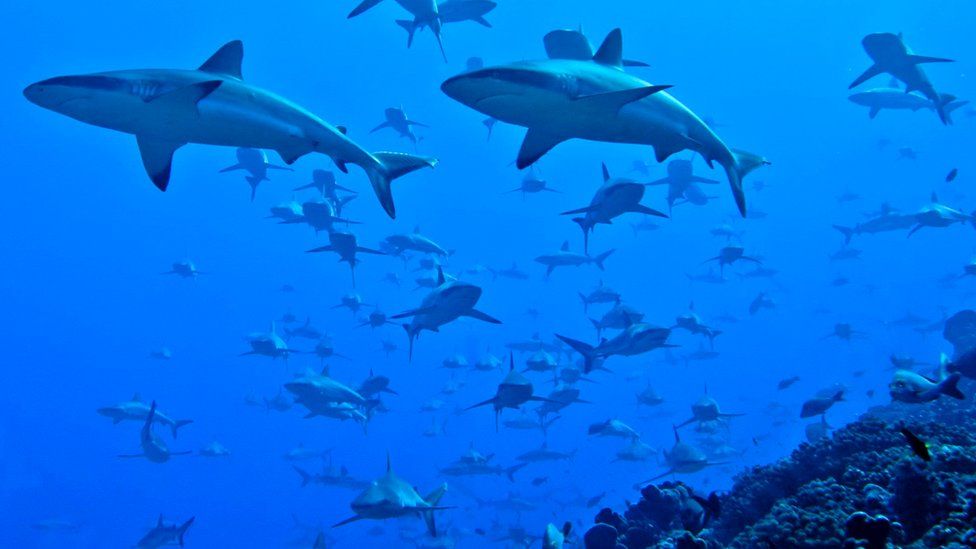

How a huge school of sharks 'flips the food pyramid' BBC News
Sharks are a diverse group of mobile predators that forage across varied spatial scales and have the potential to influence food web dynamics. The ecological consequences of recent declines in.

Sharks Fish & Chicken CLOSED Seafood 518 W Harrison St, Chicago
Sharks keep the food web in balance. Many large shark species are apex predators at the top of the ocean's food web. They're pretty flexible about what they eat, chowing down on whatever prey is plentiful and switching to other foods if a prey population is low. In this way, apex predator sharks keep the food web in balance.

Sharks, The Apex Predators — Save The Sharks
Blacktip sharks play a crucial role in marine food webs, occupying a unique ecological niche and contributing to the balance of marine ecosystems. As a predator, blacktip sharks play a significant role in controlling the populations of their prey species, which include bony fish and crustaceans. They are also preyed upon by larger predators.

Sharks and fur seals Tigtag
In this way, the sun's energy is transferred up aquatic food webs, eventually feeding apex predators such as sharks and other large fish. What factors shape food webs? Aquatic food webs can be characterized by the number of trophic levels and the amount of biomass in each level. Nutrient availability is central in shaping food webs.