
deep and superficial cardiac plexuses = sympathetic innervation to the heart
The greater petrosal nerve or superficial petrosal nerve is a branch of the nervus intermedius (nerve of Wrisberg) that carries parasympathetic, taste, and sensory fibers of the facial cranial nerve (CN VII).
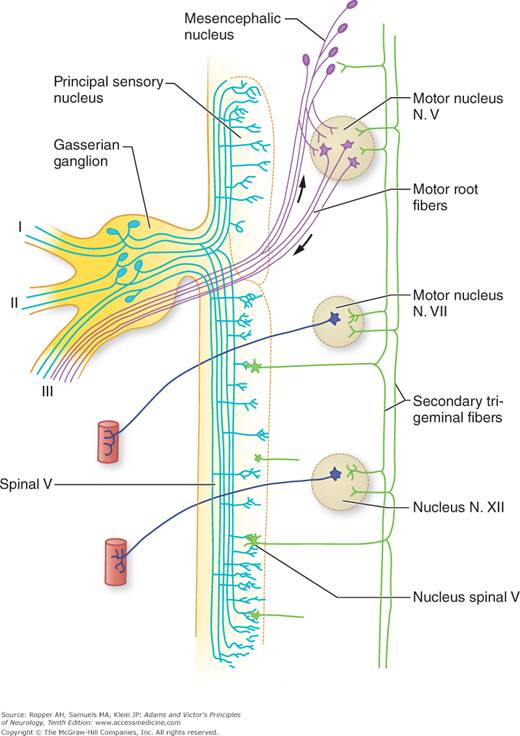
cranial nerve pathways through skull
nerve of Wris· berg -ˈriz-ˌbərg, Ger -ˈvris-ˌberk 1 : nervus intermedius 2 : a small nerve of the upper arm arising from the brachial plexus and distributed especially to the skin of the medial side Dictionary Entries Near nerve of Wrisberg nerve of Lancisi nerve of Wrisberg nerve root See More Nearby Entries Cite this Entry Style
Radiology Cases Subtle Wrisberg Rip (in setting of ACL tear)
Nerve of Wrisberg A. Birmingham Copyright and License information Disclaimer Full text Full text is available as a scanned copy of the original print version. Get a printable copy (PDF file) of the complete article (538K), or click on a page image below to browse page by page. 63 64 65 66 67 68 69

Figure 1 from A Very Rare Type of Neuralgia Nervus Intermedius Neuralgia. Semantic Scholar
1. Introduction The nervus intermedius, also known as the intermediary nerve, intermediate nerve, portio intermedia, Wrisberg's nerve, Sapolini´s nerve or intermedius nerve, is commonly described as a root of the facial nerve containing sensory and parasympathetic fibers.

14.3 Brainstem The medulla oblongata relays signals between the rest of the brain and the
The nerve of Wrisberg (named for Heinrich August Wrisberg) can refer to: Medial cutaneous nerve of arm A branch of the facial nerve, also called Nervus intermedius This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Nerve of Wrisberg.

Anatomical consideration of the cardiac plexus to prevent grave bradycardiac arrhythmias
The nerve of Wrisberg exits between the motor root and the vestibulocochlear nerve. The nerve joins the motor root as it exits the brainstem or at the porus acusticus and becomes a common trunk, the nervi facialis. The intracanalicular segment travels within the anterior and superior quadrants of the internal auditory canal (IAC) for.

Nerve of Wrisberg / Intermedius Sensory & Parasympathetic division of Facial Nerve
We read with extreme interest the article written by Burmeister et al entitled "Identification of the Nervus Intermedius Using 3T MR Imaging." 1 It is surprising that this minute nerve has gained such a wide clinical, functional, and now radiologic interest since the original description in 1778 by Wrisberg. 2 However, there is a point of concern in the article.

the structure of an ear with all its parts labeled in this diagram, you can see how it works
Nervus intermedius neuralgia, or geniculate neuralgia , corresponds to a clinical manifestation of sudden paroxysms of excruciating otalgia which usually lasts a few seconds to a few minutes, involving the nervus intermedius (intermediate nerve of Wrisberg). Epidemiology Nervus intermedius neuralgia typically occurs in middle-aged women 1.

Anatomy, Physiology, & Testing of the Facial Nerve Ento Key
The greater petrosal nerve or superficial petrosal nerve is a branch of the nervus intermedius (nerve of Wrisberg) that carries parasympathetic, taste, and sensory fibers of the facial cranial nerve (CN VII).
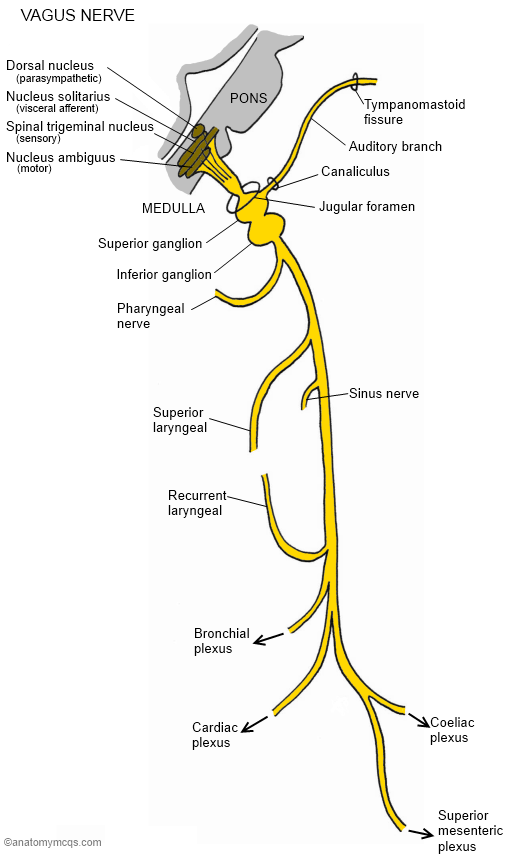
Nerve October 2015
The nervus intermedius, also known as the intermediary nerve, intermediate nerve, portio intermedia, Wrisberg's nerve, Sapolini´s nerve or intermedius nerve, is commonly described as a root of the facial nerve containing sensory and parasympathetic fibers.
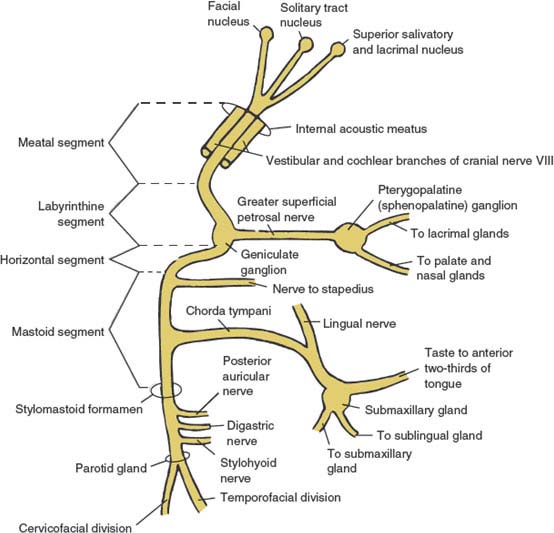
Cranial Nerve VII (The Facial Nerve) Neupsy Key
The nervus intermedius, also known as intermediate nerve of Wrisberg , is a part of the facial nerve (CN VII) which contains somatic sensory, special sensory, and visceral motor (secretomotor) fibers 1. Gross anatomy Nuclei superior salivatory nucleus 7

Clinical Questions in General Practice October 2012
The cisternal segment consists of the motor root and nervus intermedius (nerve of Wrisberg), which emerge from the brainstem and course into the internal audi-tory canal. These two portions merge at the internal auditory canal to form the canalic-ular (intracanalicular, meatal) segment.

Facial Nerve Anatomy Overview, Embryology of the Facial Nerve, Central Connections Nerve
Cardiovascular system Lymphoid organs Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Nerves Roots of nerves Ganglia Nerve plexuses Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Cervical nerves Cervical plexus Brachial plexus Supraclavicular part of brachial plexus Supraclavicular branches of brachial plexus Infraclavicular part of brachial plexus

The Peripheral Nervous System Anatomy and Physiology I
Definition The facial nerve consists of a motor and a sensory part, the latter being frequently described under the name of the nervus intermedius ( pars intermedii of Wrisberg ). The sensory root arises from the genicular ganglion, which is situated on the geniculum of the facial nerve in the facial canal, behind the hiatus of the canal.
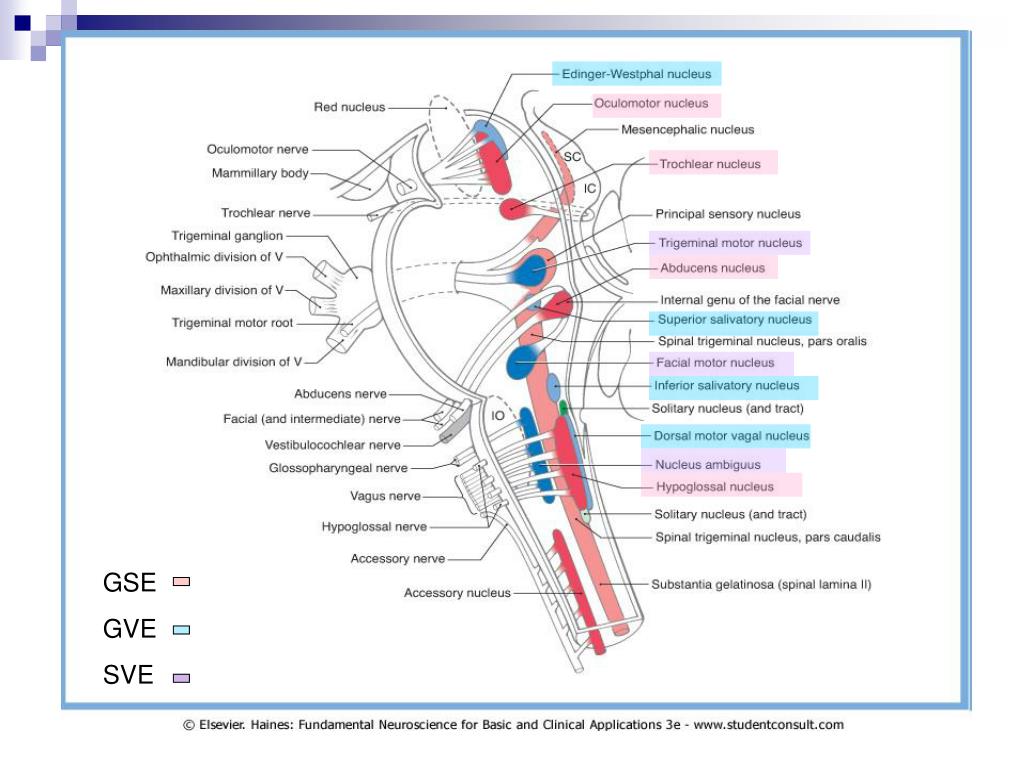
PPT Chapter 14 A Synopsis of the Cranial Nerves of the Brainstem PowerPoint Presentation
Although probably identified by Eustachius (1563), the first clearly documented description of the nervus intermedius was completed by Heinrich August Wrisberg at the University of Göttingen in 1777. In 1881, Giuseppe Sapolini defined the nervus intermedius, according to its specific features, as the 13th cranial nerve.

The Facial Nerve Human Anatomy
The intermediate nerve, nervus intermedius, nerve of Wrisberg or Glossopalatine nerve, [1] [2] [3] is the part of the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII) located between the motor component of the facial nerve and the vestibulocochlear nerve (cranial nerve VIII). It contains the sensory and parasympathetic fibers of the facial nerve.