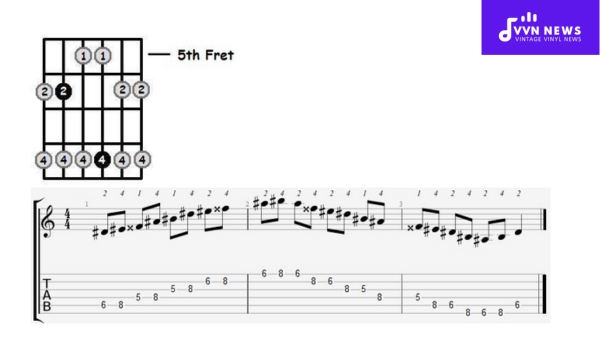
D Sharp Major Pentatonic Scale [A Bright And Positive Tone]
To find a Relative key, first determine if the key you are currently in is major or minor. If you're in a major key, you move DOWN three semitones to find the relative minor. If you're in a minor key, you move UP three semitones to find the relative major. Here is a list of all of the relative keys: Examples of Relative Keys
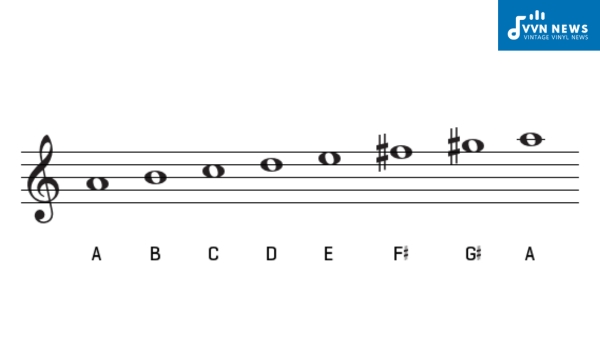
A Minor Scale [Unlock The Mysteries Of Musical Composition]
Understanding Music Relative Keys Understanding the relative major and relative Minor Watch on Relative Keys Relative keys have the same key signature (number of sharps or flats). For every note in the chromatic scale there is a relative major key and a relative minor key. Let's have a look at an example.
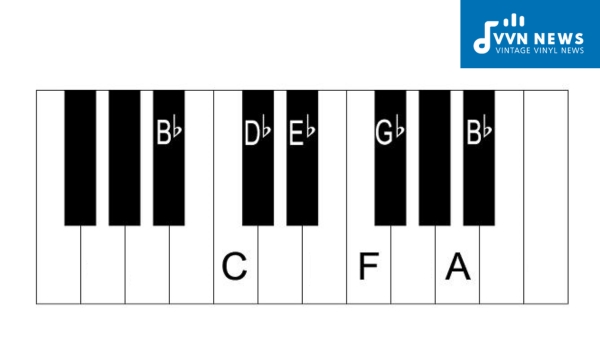
B Flat Minor Scale Explained [Learn And Experiment With Scales]
The A minor scale is called the relative minor scale of the C major scale. It's also true to say that the C major scale is the relative major of A minor; it can go both ways. Because of this relationship relative minor scales share the same key signature as their major counterparts and vice versa.
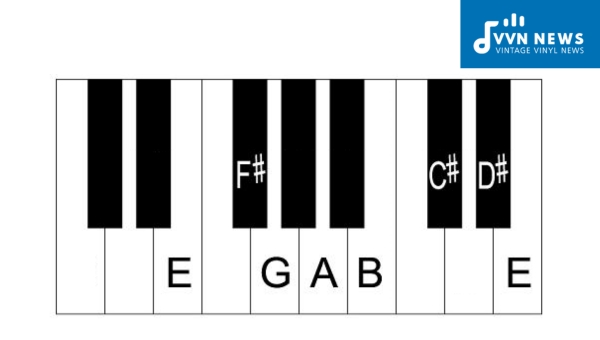
E Minor Scale Explained [Improve Your Guitar Skills Today]
To find the relative major key from a minor, take the first note of your minor key and go up three half-steps. The note you land on is now the first note of your major scale. How to find the parallel minor or major key This is even more simple than finding the relative keys.

Quick Music Theory Tip (1/8/24) Relative Minor Relative Major YouTube
Relative Minor and Relative Major Relative scales are major and minor scales that share the same notes and chords, and therefore the same key signature. Every major scale has a relative minor scale and every minor scale has a relative major scale. Finding the Relative Minor Scale

C Minor Scale [How To Master This Powerful Chord Progression]
Start learning What is the relative minor The relative minor is a minor scale that shares its key signature with a related major scale. If you start with a major scale, the relative minor is the scale that begins on the sixth degree. It shares the same key signature, so you can build it using the same notes, just in a different order.
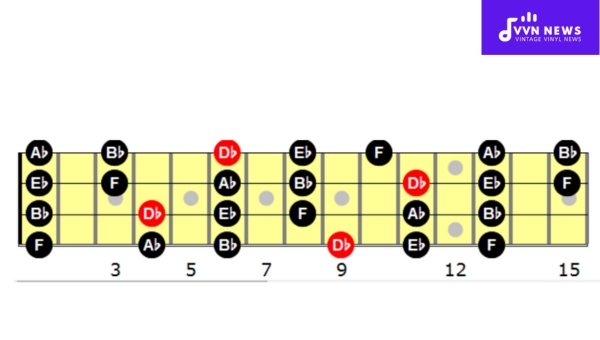
D Flat Major Pentatonic Scale [Master Its Joyful Tones]
Written by Dan Farrant Last updated 22nd September 2023 Learning about A major scale? In this post, we've put together a complete guide to everything you need to know when learning about the scale.
Melody and harmony keys, scales, modes and ornaments BBC Bitesize
Simple! To provide a couple of examples: D major - ^6 is B, so relative minor is Bm. C♯minor, ^3 is E, so relative major is E. G major - ^6 is E, so rel. min. is Em. D minor, ^3 is F, so rel. maj. is F maj.
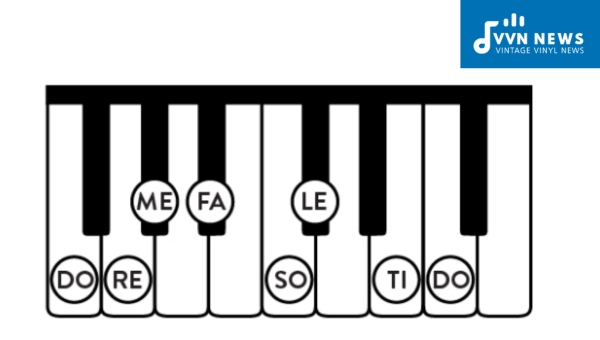
F Minor Scale Explained [StepByStep Guide To Mastering Scales]
E.g. relative minor to C major key with no accidentals in the signature, is A minor, with no accidentals as well. The corresponding scale is called natural minor, or aeolian. There is however something interesting about minor key. If you use all diatonic notes (e.g. all notes without accidentals in A-minor), the chord on the fifth step, the.

D Flat Major Scale [The Tools Of Music Theory]
Figure 6.4.4 6.4. 4: The interval patterns for major and natural minor scales are basically the same pattern starting at different points. It is easy to predict where the relative minor of a major key can be found. Notice that the pattern for minor scales overlaps the pattern for major scales. In other words, they are the same pattern starting.
Melody and harmony keys, scales, modes and ornaments BBC Bitesize
The relative minor chord is the sixth degree chord of the major key in question. For example, the C relative minor chord is the sixth degree chord of the C major key, that is, Am (or Am7). Another example: suppose the tonality is G major. The relative minor of G will be Em (or Em7).

Relative Keys & Scales Guide to Relative Major & Minor
The relative minor of A major is F# minor You can already see a pattern here: The relative minor is always a minor third (or 3 half steps) below the major. Though this is easy to remember, it doesn't yet explain, what relative minor is and why we need it. So let me ask the question: what do the major key and its relative minor have in common?

MAIKO RELATIVE MINOR MINGA ( je major scale oba maikai uni relative
A major A major (or the key of A) is a major scale based on A, with the pitches A, B, C ♯, D, E, F ♯, and G ♯. Its key signature has three sharps. Its relative minor is F-sharp minor and its parallel minor is A minor.
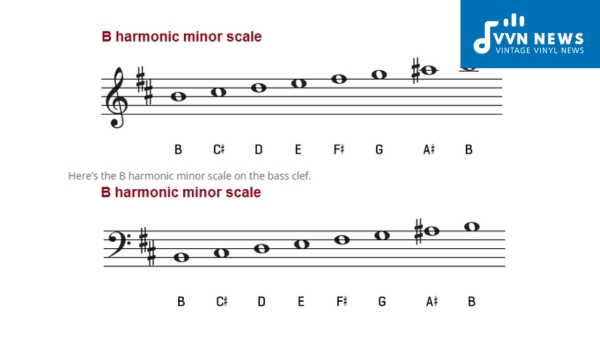
B Minor Scale Explained [Play More Expressively On Your Guitar]
In music, relative keys are the major and minor scales that have the same key signatures ( enharmonically equivalent), meaning that they share all the same notes but are arranged in a different order of whole steps and half steps. A pair of major and minor scales sharing the same key signature are said to be in a relative relationship.

Relative major and minor using the Pentatonic scale pattern YouTube
An introduction to the relative majors and minors - the key to songwriting and improvising. "Relative keys" is an important concept in music theory that's able to unlock songwriting and improvisation potential. It grants you a deeper understanding of the relationship between the major and minor scales, and how to epitomise it in an.

A Flat Minor Pentatonic Scale [Unleash Subtle Tension In Your Music]
The relative major of e minor is G major, count: E (minor), F, F#, and G (major). Now, see if you can figure out why the next scales are relatives (and for your own good, start memorizing them): The relative major of B minor is D major. The relative major of F minor is A major.