
Human Muscles Diagrams Labeled 2019 101 Diagrams
We've just released a collection of 500+ OSCE Stations! 🙌 https://geekymedics.com/osce-stations/ This video provides an overview of the muscles of facial expression using high-quality 3D.

Pin on Apocalypse
The facial muscles are striated muscles that link the skin of the face to the bone of the skull to perform important functions for daily life, including mastication and expression of emotion.

Face And Neck Muscle Diagram / Facial Muscles Images Stock Photos
Muscles of Facial Expression Blood Supply: External Carotid Artery Motor Innervation: Facial Nerve (Vll) Sensory Innervation: Trigeminal Nerve (V) Frontalis (worry muscle): Actions: Raises eyebrows, furrows brow Innervation: Facial Nerve (Vll) Origin: from galea aponeurotica Insertion: to skin above the eyebrows

Pin on Botox
1 Pull on your forehead with your index finger to smooth lines. Put your index fingers just above each of your eyes, then pull down on your eyes while trying to raise your eyebrows. Repeat 10 times to help firm your forehead. [2] This exercise helps smooth out wrinkles and fine lines.

Pin on anatomy
Anatomy Facial muscles Author: Gordana Sendić MD • Reviewer: Jana Vasković MD Last reviewed: November 21, 2023 Reading time: 27 minutes Recommended video: Muscles of facial expression [12:24] Overview of the muscles responsible for facial expression. Facial muscles (Musculi faciales)

Axial Muscles of the Head, Neck, and Back · Anatomy and Physiology
Learn and practice the facial muscles more effectively using our facial muscles quizzes and labeled diagrams.

Facial Muscles and Expressions Classic Human Anatomy in Motion The
Muscles and Tendons Information Center Reviewed By: Pramod Kerkar, M.D., FFARCSI, DA There are about 20 flat skeletal muscles that construct the facial structure. All of these muscles have different functions in the face. Innervated by the cranial nerve, which is the facial nerve, the muscles control all of our facial expressions.

Anatomy of the facial muscles. Reprinted under Creative Commons
Interactive diagram of the muscles of facial expression, including the frontalis, temporalis, orbicularis oculi, zygomaticus major, zygomaticus minor, nasalis, levator labii superioris, masseter, levator anguli oris, buccinator, obicularis oris and others.

Jeff Searle Head muscles, Human body anatomy, Facial muscles anatomy
Facial Muscles Facial muscles work together to control the parts of your face. They are essential to chewing and making facial expressions. If you experience weakness or paralysis in your face muscles, seek medical attention. Although facial palsy can be a sign of a temporary, curable condition, it may also indicate a serious medical problem.

Vintage Human Anatomy Muscles (Face, Head, Neck) Poster
Go to: Structure and Function The anatomy of the face can divide into three main regions: upper face, middle face, and lower face. The entire face is covered by skin superficially, while the deep anatomy contains muscles, fat pads, nerves, vessels, and bones. Upper Face
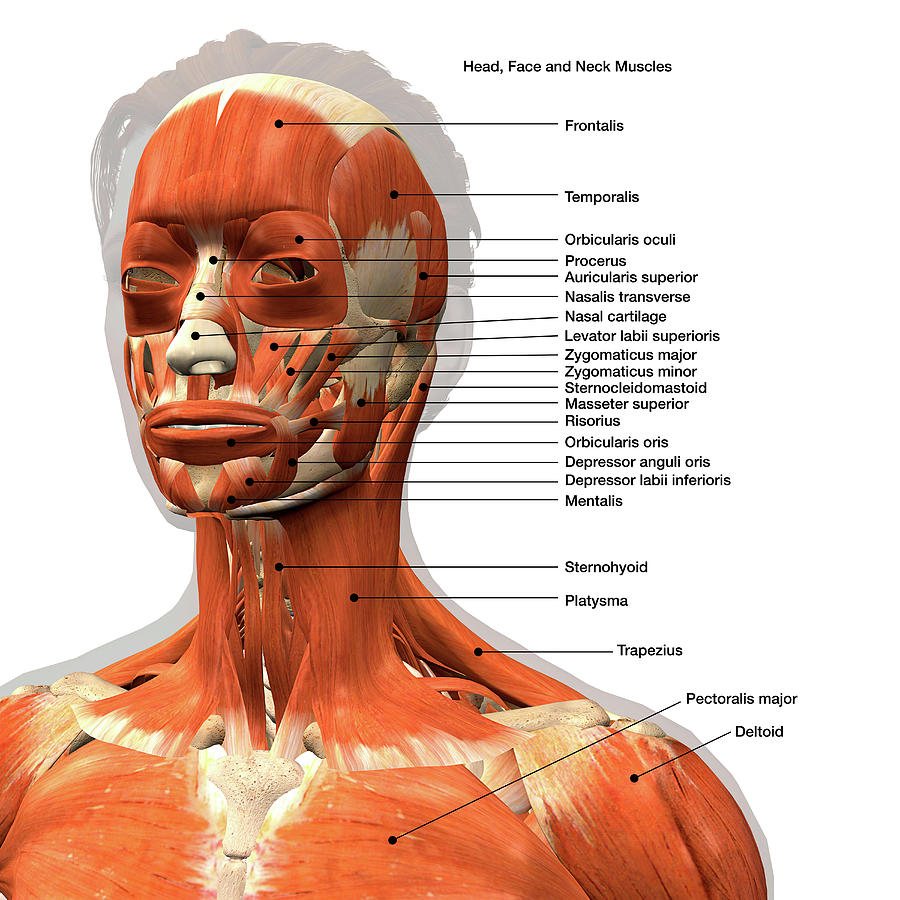
Labeled Chart Of The Facial Muscles Photograph by Hank Grebe Fine Art
The neck muscles, including the sternocleidomastoid and the trapezius, are responsible for the gross motor movement in the muscular system of the head and neck. They move the head in every direction, pulling the skull and jaw towards the shoulders, spine, and scapula. Working in pairs on the left and right sides of the body, these muscles.

Muscles of Face Anatomy Flashcards Anatomic.us Muscles of Face
Face muscle anatomy Test your information with labeled diagrams Practice test Interactive headmost muscles quizzes Sources + Show choose Face string anatomy

Head Muscles Diagram Face muscles anatomy, Anatomy
Key Terms. depressor labii inferioris: An analogous muscle that lowers the bottom lipEndFragment; Buccinator: This muscle is located between the upper and lower jaws in the cheek, deep to the other muscles of the face.; zygomatic: This muscle controls the cheeks to create smiles and frowns.; Procerus: The most superior of all facial muscles.; depressor anguli oris: This muscle is opposite to.

Pin on Anatomy for Sculpture The Human Neck
The facial muscles can broadly be categorised into three groups - orbital, nasal and oral. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the muscles of facial expression - their attachments, actions and clinical relevance. Fig 1 - Innervation to the muscles of facial expression via the facial nerve (CN VII) Orbital Group

fac06_15FigureL.jpg (1360×1050) Neck muscle anatomy, Facial muscles
The human face is the most anterior portion of the human head. It refers to the area that extends from the superior margin of the forehead to the chin, and from one ear to another. The basic shape of the human face is determined by the underlying facial skeleton (i.e. viscerocranium ), the facial muscles and the amount of subcutaneous tissue.

Pin on Acrylic painting techniques
The facial muscles are a group of striated skeletal muscles supplied by the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII) that, among other things, control facial expression. These muscles are also called mimetic muscles. They are only found in mammals, although they derive from neural crest cells found in all vertebrates.